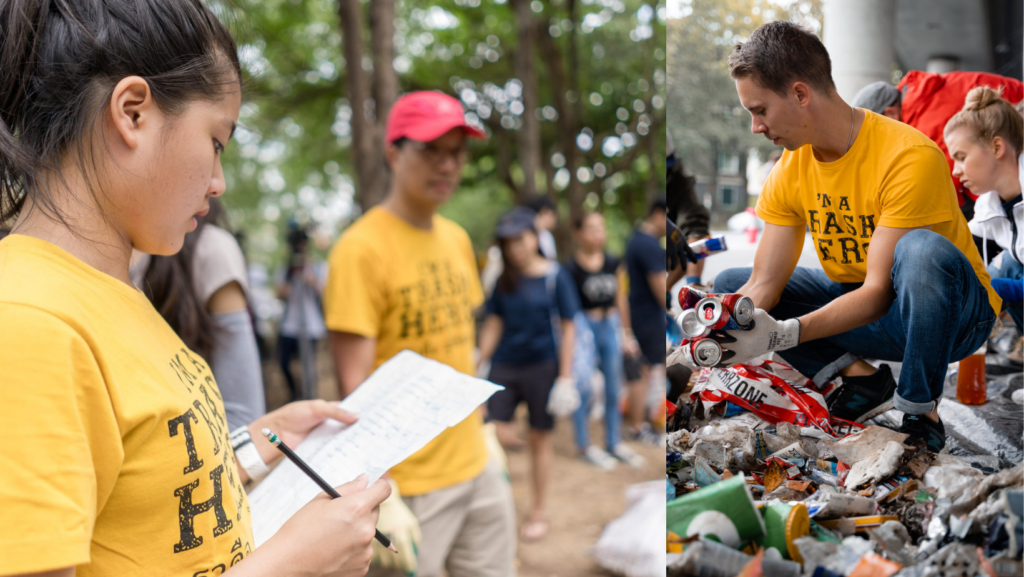
Selamat datang, Trash Hero!
Terima kasih telah bergabung bersama kami. Apakah Anda siap untuk melakukan perubahan?
Apa yang kita lakukan akan menginspirasi orang lain untuk peduli terhadap lingkungan dan untuk mengubah kebiasaan. Perubahan ini akan menyebar ke seluruh lapisan masyarakat, sehingga nantinya kita akan hidup di dunia yang bersih dari sampah plastik.
Kami akan menunjukkan pada Anda tentang bagaimana melakukan aksi tersebut…
CONTENTS
Pendahuluan
1. Membangun tim
2. Bahan marketing
3. Menyiapkan program aksi bersih
– Where does the trash go?
– True and false solutions for waste
4. Menjalankan program botol minum isi ulang
5. Mempersiapkan program tas pakai ulang
6. Melibatkan anak-anak
7. Menjangkau masyarakat secara lebih luas
8. Menggunakan media sosial & media konvensional
9. Mendapatkan sponsor
10. Mengelola relawan
11. Pantang menyerah!
12. Mendukung misi Trash Hero yang lebih luas
Perbaruan terakhir: Oktober 2020
Pendahuluan
TRASH HERO: Memberi inspirasi tentang penanganan sampah
Trash Hero adalah sebuah gerakan global, yang dikelola oleh relawan.
Misi kami adalah mengajak masyarakat untuk secara bersama-sama membersihkan dan menghindari produksi sampah – dan terutama menciptakan Bumi yang bebas sampah.
Didirikan di Thailand pada tahun 2013, saat ini kami aktif di lebih dari 100+ lokasi di seluruh dunia, melalui jaringan chapter lokal dan organisasi negara.
Induk dari organisasi ini terdaftar di Swis dengan nama Trash Hero World, yang merupakan sebuah organisasi nirlaba.
Apa yang kami lakukan
Kami memiliki tiga program kerja utama, yang keseluruhannya dijalankan oleh para relawan:
 Aksi Bersih
Aksi Bersih
Kami menyelenggarakan kegiatan mingguan di mana kami memungut sampah, mengundang, serta memotivasi masyarakat untuk menjadi bagian dari Trash Hero.
 Program Botol dan Tas Pakai Ulang
Program Botol dan Tas Pakai Ulang
Kami menyediakan botol stainless steel yang dapat dijual oleh pebisnis lokal. Pebisnis akan mendapat untung dari penjualan tersebut, dengan timbal balik berupa penyediaan air minum isi ulang secara gratis di lokasi bisnis mereka. Sebagai tambahan, kami juga memproduksi tas belanja pakai ulang dengan harga yang terjangkau bagi pebisnis lokal untuk dijual kembali.
 Pendidikan dan Anak-anak
Pendidikan dan Anak-anak
Kami memiliki buku cerita untuk anak-anak yang kami buat sendiri yang dilengkapi dengan panduan tantangan dan penghargaan, dan kami mengunjungi sekolah-sekolah dan membawakan pelatihan guna meningkatkan kesadaran dan memperkenalkan solusi-solusi sederhana akan permasalahan lingkungan.
Bagaimana kami melakukannya
Pendekatan yang dilakukan oleh Trash Hero didasarkan pada lima prinsip berikut:
- Positif: kami fokus pada solusi (bukan masalah), pada masa depan (bukan masa lalu), dan pada apa yang berjalan dengan baik (bukan pada siapa yang salah atau siapa yang layak disalahkan).
- Terbuka dan netral: kami bekerja secara mandiri, membawa masyarakat bersama-sama menuju tujuan yang menguntungkan semua pihak.
- Tunjukkan, bukan mengajarkan, lalu ulangi: kami memberi contoh, mengambil langkah kecil yang jika dilakukan secara berulang-ulang akan menghasilkan sesuatu yang besar. Dengan kegiatan yang dilakukan secara rutin, perubahan yang terjadi akan bertahan lama.
- Berpikir secara global, beraksi secara lokal: chapter-chapter lokal kami adalah tulang punggung pergerakan kami. Trash Hero World menyediakan pelatihan, materi penunjang, dan perangkat global untuk memperkuat aspirasi mereka.
- Tidak melibatkan uang: chapter-chapter lokal kami tidak memungut biaya atau mengambil keuntungan dari kegiatan-kegiatan mereka. Pengeluaran dibiayai oleh donasi dalam bentuk barang dan jasa dari sponsor lokal, dan semua produk dijual sesuai dengan harga produksinya, dengan resi yang bisa dipertanggungjawabkan secara publik.
Apa yang chapter Trash Hero lakukan?
Chapter-chapter lokal kami membawa misi dan pendekatan Trash Hero kepada komunitas mereka masing-masing. Mereka bisa menyelenggarakan sebagian atau semua kegiatan yang dijelaskan di atas, dengan paling tidak menjalankan kegiatan aksi bersih secara rutin dan program botol.
Siap? Ayo kita mulai!
“Dengan mengubah gaya hidup kita, kita berperan dalam menjaga keselamatan dan kesejahteraan manusia, dan terutama juga keselamatan Bumi”
Jeremy Irons, Produser Eksekutif Film “Trashed”
⬆ Kembali ke atas ⬆
1. Membangun tim
 Tim yang baik adalah syarat penting dari kesuksesan sebuah chapter. Paling tidak sebuah tim memiliki 3 orang anggota, termasuk paling tidak satu orang yang terhubung secara baik dengan komunitas lokal. Jumlah optimal anggota sebuah tim adalah 5-6 orang.
Tim yang baik adalah syarat penting dari kesuksesan sebuah chapter. Paling tidak sebuah tim memiliki 3 orang anggota, termasuk paling tidak satu orang yang terhubung secara baik dengan komunitas lokal. Jumlah optimal anggota sebuah tim adalah 5-6 orang.
Anggota tim tidak harus merupakan orang yang sudah Anda kenal sebelumnya: Anda bisa mengajak serta orang sekitar, atau membuat post di sosial media untuk menjaring orang yang tertarik untuk membantu.
Carilah orang-orang yang memiliki perilaku dan energi yang positif, yang menghormati kebudayaan lokal, dan (jika memungkinkan) yang dapat berkomitmen untuk meluangkan beberapa jam pada setiap minggu pada jangka waktu yang lama. Catatan: Jika Anda berusia di bawah 18 tahun, Anda perlu didampingi oleh seorang anggota dewasa dalam tim.
Anggota tim tidak harus merupakan seorang ahli di bidang tertentu, dan tim mentor kami akan memandu Anda untuk berkembang.
Tim Anda akan melakukan beberapa tugas pada setiap pekan:
Membuat perencanaan: Mengatur kegiatan dan program, termasuk menyediakan peralatan untuk kegiatan aksi bersih, menyiapkan pengangkutan sampah, dan juga (bila perlu) transportasi peserta.
Komunikasi: Menjawab email, pesan dan telepon; mem-post kegiatan dan update baru di Facebook (dan media sosial lainnya); mewakili Trash Hero di khalayak masyarakat dan media. Misalnya memberi pengarahan sebelum kegiatan aksi bersih dilaksanakan, atau menjadi narasumber pada wawancara dengan TV lokal.
Melibatkan masyarakat: Menginformasikan kepada pebisnis setempat mengenai kegiatan chapter Anda dan meminta dukungan mereka – contohnya dengan memasang poster iklan kegiatan chapter Anda, atau menyediakan alat dan jasa yang dibutuhkan oleh chapter Anda. Berbincanglah dengan pemerintah setempat, sekolah, dan kelompok masyarakat lainnya mengenai kegiatan chapter Anda.
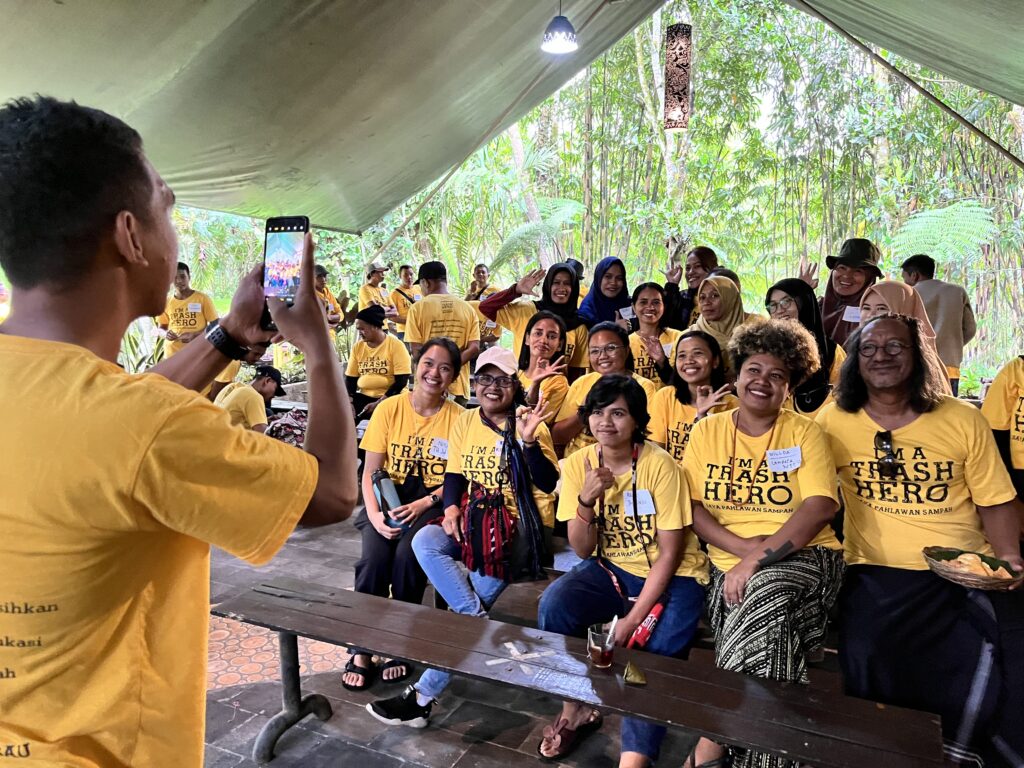
Berbagi cerita: Ambil gambar dan video untuk menjelaskan apa yang Anda lakukan dan untuk menginspirasi orang lain untuk ikut bergerak. Gambar dan video dapat di-post di media sosial, dengan menyertakan tulisan dalam bahasa lokal dan Bahasa Inggris. Bila Anda dapat menyunting/mendesain secara profesional atau memiliki peralatan memadai, itu akan menjadi nilai tambah – namun yang paling penting adalah Anda memiliki foto dan video yang positif untuk di-post.
Tidak ada cara yang baku dalam menjalankan tugas ini. Beberapa tugas dapat dikerjakan oleh lebih dari satu anggota tim, atau satu anggota dapat mengerjakan beberapa tugas. Tugas dapat dibagi menjadi beberapa pekerjaan yang lebih mudah.
Hal ini bergantung pada seberapa besar tim Anda, karakter anggota di tim Anda, dan waktu yang mereka miliki.
Selalu terbuka untuk mengundang anggota baru untuk bergabung dengan tim Anda, dan berikan tugas kecil untuk mereka. Sebagai contoh, seorang anggota baru dapat membantu sekitar dua jam per minggu untuk menerjemahkan tulisan di Facebook. Tim akan berkembang secara alami dengan cara ini.
Bila Anda harus meninggalkan tim, informasikanlah sejak jauh hari kepada anggota lain dalam tim. Akan lebih baik apabila Anda membantu mencarikan dan melatih anggota baru untuk mengerjakan tugas-tugas Anda.
Ceritakan pencapaian kesuksesan chapter Anda kepada seluruh tim – anggota tim tidak boleh menyatakan bahwa kesuksesan tersebut adalah pencapaian pribadinya, baik secara rahasia maupun di depan publik. Tunjukkan apresiasi kepada anggota tim satu sama lain, rayakan secara bersama-sama, dan chapter Anda akan tumbuh semakin kuat.

“Semua orang bisa menjadi Trash Hero”
⬆ Kembali ke atas ⬆
2. Bahan marketing
Ringkasan
Brand “Trash Hero” adalah sesuatu yang tercipta dengan usaha yang sangat keras. Brand ini mencakup nama dan logo (yang terdaftar sebagai merek dagang di seluruh dunia), juga warna, desain, dan pesan yang disampaikan. Brand ini mewakili diri kita dan apa yang kita perjuangkan. Sangatlah penting bagi kita untuk menjaga bagaimana brand ini digunakan dan memastikan bahwa brand ini digunakan secara konsisten di mana pun.
 Kita memiliki pedoman atas penggunaan logo, warna, dan font di sini, beserta beberapa template untuk digunakan sebagai bahan marketing penting. Anda dapat memperoleh akses untuk mengunduh template ini setelah chapter Anda terbentuk.
Kita memiliki pedoman atas penggunaan logo, warna, dan font di sini, beserta beberapa template untuk digunakan sebagai bahan marketing penting. Anda dapat memperoleh akses untuk mengunduh template ini setelah chapter Anda terbentuk.
Bila Anda memiliki ide untuk membuat materi marketing baru, atau membutuhkan bantuan untuk menggunakan template, Anda bisa meminta bantuan kepada tim desain kami. Mohon dimengerti bahwa mereka juga relawan seperti Anda, sehingga mereka mungkin membutuhkan waktu untuk menyelesaikan permintaan Anda. Bila Anda ingin menciptakan sendiri materi marketing yang baru, Anda perlu berkomunikasi dengan mereka terlebih dahulu sebelum mencetak / menyebarluaskannya.
1. Logo Chapter
Ketika Anda memulai sebuah chapter, kami akan membuatkan Anda sebuah laman Facebook, menggunakan logo Trash Hero dengan latar berwarna putih dan nama chapter Anda. Warna putih menandakan bahwa chapter Anda berada pada fase awal.
Setelah Anda menyelesaikan tahap uji coba – biasanya sekitar 10 kali aksi bersih – Anda diperbolehkan menggunakan logo dengan latar berwarna kuning dan laman Facebook chapter Anda akan terdaftar pada situs kami.
2. Kaos
Ketika Anda memulai chapter Anda, bila Anda berada di negara di mana sudah terdapat Trash Hero, kami akan menyediakan 1-5 kaos untuk tim inti Anda. Bila chapter Anda adalah chapter Trash Hero pertama di negara Anda, Anda perlu menunggu sedikit lebih lama hingga tersedianya stok kaos di negara Anda.
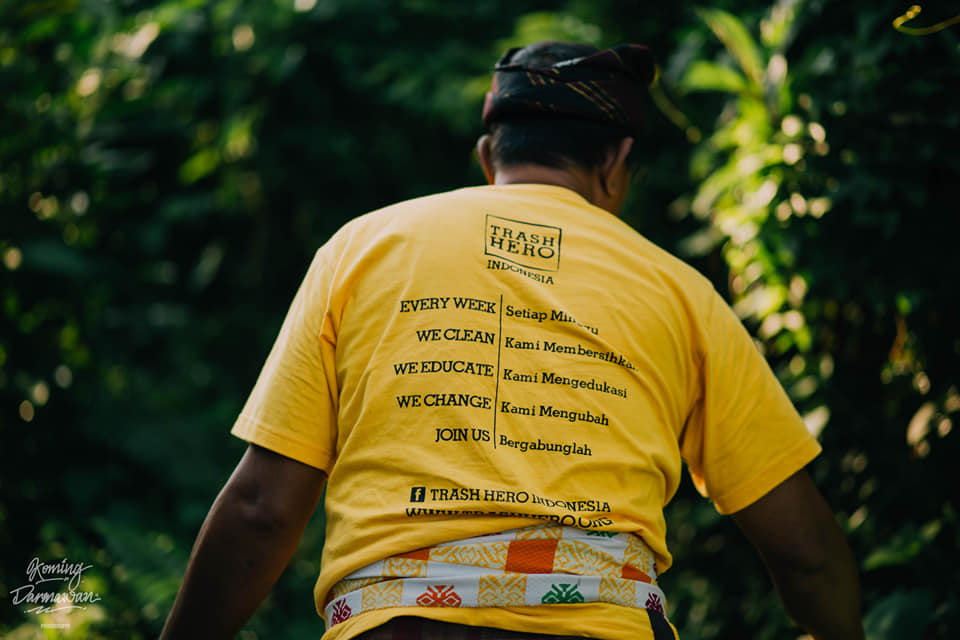

Apa itu kaos Trash Hero?
Kaos Trash Hero adalah simbol utama dari pergerakan kami. Kaos Trash Hero berwarna kuning dan di bagian depannya bertuliskan “I’m Trash Hero” dalam Bahasa Inggris.
Pada kaos juga juga terdapat terjemahan dalam bahasa lokal di bawah tulisan ber-Bahasa Inggris. Bagian belakang dari kaos dapat berbeda antara satu chapter dengan chapter lain, namun harus memiliki logo Trash Hero Indonesia, alamat website, dan laman Facebook chapter.
Tidak diperkenankan untuk mencantumkan nama atau logo pihak ketiga pada kaos Trash Hero guna menjaga kenetralan organisasi. Begitu pula sebaliknya, tidak diperkenankan untuk mencantumkan logo Trash Hero di kaos lain. Untuk mendapatkan desain kaos per chapter, Anda bisa menghubungi tim desain kami.
Pencetakan Kaos
Disarankan pencetakan kaos pertama untuk chapter Anda dilakukan setelah chapter Anda mendapatkan logo berwarna kuning. Usahakan untuk mendapatkan sponsor lokal untuk membiayai proses pencetakan, sebagai salah satu cara untuk melibatkan bisnis lokal pada kegiatan chapter Anda. (Lihat: Cara mendapatkan sponsor).
Bila memungkinkan, cetaklah kaos di perusahaan percetakan lokal untuk membangun hubungan baik dengan masyarakat lokal. Perusahaan tersebut harus memiliki bahan kaos dengan warna kuning yang sama dengan yang kami gunakan, yang terbuat dari bahan 100% katun atau bahan alami lainnya.
Pastikan berapa jumlah pemesanan minimal, dan bila memungkinkan, lakukan pembandingan harga dengan perusahaan percetakan lain. Bila tidak terdapat perusahaan percetakan di lokasi Anda, Anda bisa menghubungi koordinator Trash Hero di negara Anda untuk mendapat bantuan.
Perlu dicatat: selalu pastikan Anda mendapat nota tagihan yang menyertakan nama chapter Anda dan kirim pembayaran secara langsung kepada perusahaan percetakan. Anda akan membutuhkan nota tagihan dan nota pembayaran ini untuk dilaporkan kepada sponsor, dan juga ketika Anda menjual kaos ini kelak. Dengan begini, Trash Hero akan 100% transparan.
Trash Hero juga akan, dalam kondisi operasional yang stabil, menyediakan t-shirt gratis untuk chapter Anda.
Penjualan kaos
Kaos Trash Hero dijual sesuai harga produksi, atau diberikan secara gratis. Harga produksi dapat mencakup biaya pengiriman bila kaos tidak dicetak di wilayah sekitar Anda. Simpan bukti pembayaran yang Anda terima dari perusahaan percetakan dan jasa pengiriman, lalu publikasikan di media sosial untuk menunjukkan bahwa Anda tidak mengambil keuntungan dari proses ini.
Dana yang diterima dari penjualan kaos Trash Hero harus disimpan dan digunakan untuk mencetak kaos baru, tidak untuk keperluan lainnya. Hal ini perlu dilakukan guna memastikan selalu tersedianya kaos untuk chapter Anda.
Beberapa chapter mungkin berniat untuk menjual kaos melalui pihak ketiga seperti toko atau hotel. Sekali lagi, silakan menjual kepada mereka sesuai harga produksi, dan simpan tanda bukti pembayaran sebagai bukti. Trash Hero tidak menentukan harga jual kaos oleh pihak ketiga.
3. Materi lainnya
Terdapat beberapa materi marketing yang dapat digunakan oleh chapter Anda, termasuk:
- Poster: untuk mengiklankan kegiatan aksi bersih atau program isi ulang air minum di restoran, toko, hotel, dll di wilayah Anda
- Spanduk atau bendera: untuk digunakan saat kegiatan atau pengambilan foto
- Kartu nama
Tidak semua barang di atas diperlukan oleh setiap chapter.
Sekali lagi, tim desain dapat membantu Anda. Bila Anda lebih suka menggunakan desain Anda sendiri, Anda bisa melakukannya dengan mengikuti petunjuk brand dan mengirim hasil desain kepada tim desain untuk diperiksa sebelum dicetak.
Usahakan untuk mencetak di percetakan setempat: beberapa badan usaha mungkin akan bersedia memberikan potongan harga atau bebas biaya untuk organisasi seperti Trash Hero (jangan malu untuk bertanya!). Atau, temukan sponsor untuk membiayai proses produksi.
Pertimbangkan bahan yang Anda gunakan: kertas daur ulang dan kain katun akan lebih baik dibanding vinyl, polyester, atau papan berlapis plastik.
⬆ Kembali ke atas ⬆
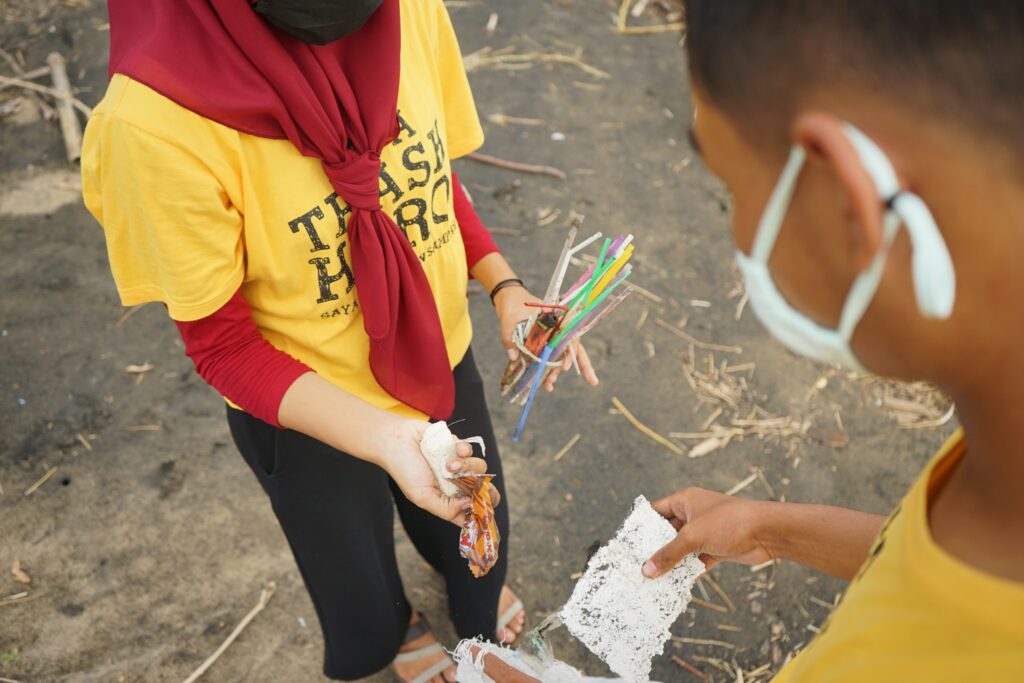
3. Menyiapkan program aksi bersih
Chapter Trash Hero melakukan aktivitas bersih mingguan. Hal ini menciptakan kesadaran berkesinambungan di dalam komunitas dan menciptakan dasar bagi perubahan tingkah laku. Aksi bersih juga memungkinkan kami untuk mengumpulkan data yang dapat diolah oleh para ilmuwan dan organisasi advokasi untuk mempengaruhi para perusahaan dan pemerintah untuk “menutup keran sampah plastik.”
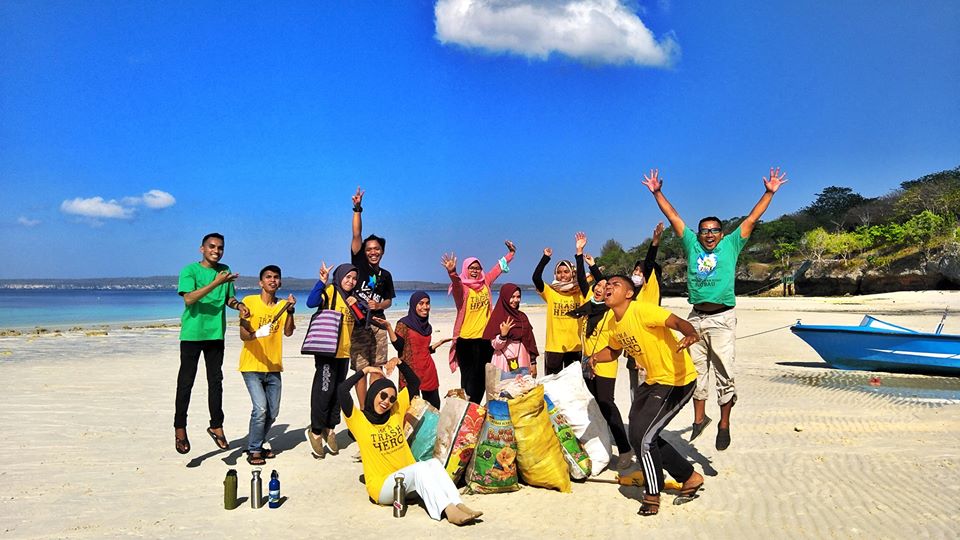

Di mana kita melakukan aksi bersih?
Di beberapa tempat, sampah ada di mana-mana. Jika Anda tinggal di dekat pantai atau area publik terbuka, tempat-tempat ini adalah tempat yang sangat bagus untuk memulai kegiatan aksi bersih; hindari jalanan yang ramai atau tempat lainnya yang mungkin berbahaya bagi para relawan.
Penting: Kita hanya membersihkan area umum. Kita tidak membersihkan area milik pribadi.
Perijinan
Sebelum memulai kegiatan aksi bersih, cobalah hubungi pemerintah setempat dan mintalah izin untuk melakukan aksi bersih di wilayah tersebut.
Menentukan hari dan waktu
Pilihlah satu hari dalam setiap minggu serta waktu yang sekiranya cocok dengan waktu luang yang dimiliki oleh anggota tim dan orang-orang di wilayah sekitar.
Contoh: Setiap hari Minggu pukul 4 sore. Pertimbangkan juga faktor cuaca: matahari bisa sangat terik pada tengah hari.
Catatan: Mengatur jadwal aksi bersih mingguan dapat menjadi sebuah tantangan besar. Jika tim Anda mengalami kesulitan, bersabarlah. Mulailah dengan aksi bersih dengan jadwal yang lebih longgar, misalnya 2 minggu sekali, sambil membiasakan diri dan berjuang agar bisa menjalankan aksi bersih setiap minggu. Saat Anda memiliki cukup pengalaman dan tim Anda telah berkembang, hal ini akan lebih mudah dilakukan.
Menentukan titik pertemuan
Anda dapat menyelenggarakan aksi bersih di lokasi yang sama atau di lokasi yang berbeda- beda pada setiap minggunya. Terdapat dua strategi yang berbeda untuk setiap aksi tersebut:
“Titik pertemuan yang tetap”: strategi ini akan sangat berguna misalnya jika Anda tinggal di sebuah pulau kecil, atau jika Anda membersihkan area yang sama setiap minggunya (contoh: di sebuah pantai). Hal ini akan memudahkan orang untuk menemukan lokasi aksi bersih dan akan efektif jika disebarkan melalui poster dan media iklan lainnya, sebagai contoh, poster dapat bertuliskan seperti ini: “Bergabunglah dengan kami setiap hari Senin pukul 4 sore di Pantai Batu Bolong.”
“Titik pertemuan yang berubah-ubah”: Jika Anda mengubah lokasi aksi bersih setiap minggunya, Anda harus menginformasikan orang-orang melalui media sosial mengenai lokasi aksi bersih selanjutnya. Buatlah sebuah event pada laman Facebook chapter Anda dan undanglah semua orang untuk datang (lihat juga: Menggunakan media sosial). Poster dapat bertuliskan seperti ini: “Kami membersihkan Jakarta setiap hari Minggu pukul 10 pagi. Lokasi detail dapat dilihat melalui Facebook kami.”
Apapun strategi yang Anda pilih, hari dan waktu aksi bersih mingguan harus selalu sama setiap minggunya dan tempat yang dipilih sebagai titik temu harus bersifat netral (contoh: pantai, patung, jalan, stasiun kereta), jangan memilih tempat yang mempromosikan sebuah bisnis (contoh Green Hostel, Hippo Bar, Marco’s Pizza).
 Menginformasikan kegiatan aksi bersih kepada orang-orang
Menginformasikan kegiatan aksi bersih kepada orang-orang
Ada beberapa cara untuk membuat orang berpartisipasi:
- Dari mulut ke mulut: berbincanglah dengan orang sebanyak mungkin
- Posters: mintalah tim desain kami untuk membuat sebuah poster, carilah percetakan lokal untuk mencetaknya, dan pasanglah poster di bagian dalam ruangan di tempat bisnis-bisnis yang mendukung kegiatan Anda (di luar ruangan biasanya poster tidak bertahan lama)
- Media sosial: buatlah sebuah post di halaman Facebook chapter Anda dan grup-grup Facebook lainnya (lihat: Media sosial)
- Kaos Trash Hero: bagian belakang kaos dapat digunakan untuk mempromosikan kegiatan Anda (lihat: Bahan marketing)
- Undangan: Anda dapat mengirimkan undangan kepada pihak hotel atau bisnis lain untuk mengirim pegawai mereka turut serta dalam aksi bersih.
Pastikan seluruh informasi terkait aksi bersih telah tercantum: tanggal, waktu dan tempat; juga informasi bahwa setiap orang boleh bergabung hanya dengan datang ke lokasi. Kita menggunakan slogan: “No cost, no sign-up, just show up!” yang berarti “Tidak perlu membayar, tidak perlu daftar, cukup datang saja!”
Apa yang harus disiapkan sebelum aksi bersih?
Alat dan bahan
Kebutuhan dasar:
- Sarung tangan (gunakan sarung tangan yang dapat dicuci dan tahan lama, bukan sarung tangan plastik sekali pakai)
- Kantong sampah (gunakan kantong yang tahan sekali pakai)
- Peralatan P3K
Akan lebih baik jika hal ini bisa disediakan:
- Air* dari wadah yang dapat digunakan kembali (bukan botol plastik) dan makanan ringan yang tidak menghasilkan sampah (contoh: pisang, bukan kue yang dikemas dengan plastik) bagi para relawan
- Timbangan (untuk mengukur berat sampah yang terkumpul)
- Beberapa alat bantu (di area tertentu alat pencapit sampah, garu, pisau atau sekop mungkin saja dibutuhkan)
- Spanduk atau bendera chapter Trash Hero (dapat digunakan sebagai properti foto)
- Selotip dan spidol untuk memberi label di karung sampah untuk memudahkan dinas pengolah sampah dalam mengelola sampah mereka
*Terlepas dari apakah Anda menyediakan isi ulang air minum atau tidak, selalu ingatkan para relawan untuk membawa minum mereka sendiri di kegiatan aksi bersih, jangan sampai relawan kita mengalami dehidrasi!
Pengelolaan relawan & perencanaan
Pada beberapa aksi bersih pertama, ajaklah setidaknya dua orang di dalam tim untuk membantu Anda. Tugas mereka meliputi memberikan penjelasan kepada relawan baru, dokumentasi, penimbangan sampah dan lain sebagainya. Di kemudian hari, relawan lain yang sering datang dapat membantu Anda dalam tugas-tugas ini.
Atur penjemputan sampah hasil aksi bersih
Sampah dapat diberikan kepada dinas pengelola sampah setempat atau dikirim ke pusat daur ulang atau tempat pembuangan sampah resmi. (lihat: Kemana sampah diangkut?)
Transportasi
Pada umumnya orang-orang diharapkan untuk datang sendiri ke lokasi aksi bersih, namun sebagai contoh jika Anda akan membersihkan sebuah area yang yang lokasinya jauh dari tempat tinggal para relawan, sebaiknya Anda menyediakan transportasi dua arah bagi mereka.
Bagaimana cara mengorganisir alat penunjang, penjemputan sampah, atau transportasi
Idealnya, seluruh hal ini dapat disediakan oleh komunitas lokal Anda. Jika seluruh anggota komunitas bekerja bersama, setiap orang dapat berkontribusi dan berbagi tugas dan menghasilkan hasil yang baik.
 Ada beberapa kemungkinan cara kerjasama: pelaku usaha daerah atau dinas kota dapat membantu menyediakan beberapa alat kebersihan, dinas kebersihan setempat dapat membantu dalam penjemputan sampah, restoran atau hotel dapat memberikan air atau makanan bagi relawan, pengusaha laundri lokal dapat mencuci sarung tangan, dan pihak-pihak lain yang mungkin membantu. (Lihat: Cara mendapat sponsor).
Ada beberapa kemungkinan cara kerjasama: pelaku usaha daerah atau dinas kota dapat membantu menyediakan beberapa alat kebersihan, dinas kebersihan setempat dapat membantu dalam penjemputan sampah, restoran atau hotel dapat memberikan air atau makanan bagi relawan, pengusaha laundri lokal dapat mencuci sarung tangan, dan pihak-pihak lain yang mungkin membantu. (Lihat: Cara mendapat sponsor).
Gambaran besarnya adalah setiap orang dapat berkontribusi dan menjadi bagian dari Trash Hero. Bagi sebuah usaha, hal ini dapat menjadi publikasi iklan dan branding dengan biaya rendah. Kita akan selalu mengucapkan terima kasih di hadapan publik kepada para sponsor yang berkontribusi dan memuatnya di kemudian hari melalui media sosial kita.
Penting sekali untuk melibatkan sebanyak mungkin pelaku bisnis, dengan jenis dukungan yang berbeda-beda setiap minggunya. Gunakanlah cara yang kreatif, misalnya, pengusaha spa dapat memberikan voucher spa gratis sebagai hadiah bagi para relawan. Dengan banyaknya dukungan dari sponsor lokal (baik besar maupun kecil), masyarakat kemudian akan paham bahwa Trash Hero adalah gerakan yang netral untuk kebaikan bersama.
Sangatlah penting untuk hanya menerima donasi berbentuk barang dan jasa, bukan berupa uang. Sebagai contoh jika Anda membutuhkan sarung tangan, mintalah bantuan penyediaan sarung tangan. Terkadang bisnis lebih cenderung ingin menyumbang dalam bentuk uang. Dalam kasus seperti ini, belilah terlebih dahulu sarung tangan tersebut lalu berikan nota pembelian tersebut kepada sponsor untuk mendapat donasi sejumlah nilai pembelian. Hal ini perlu dilakukan untuk memastikan agar segala hal berjalan secara transparan dan semua orang percaya bahwa chapter Trash Hero tidak mendapatkan dana melalui donasi.
Hari H: perencanaan aksi bersih rutin
Berikut adalah beberapa poin yang harus dijelaskan pada tim Anda sebelum Anda memulai aksi bersih — juga harus dikomunikasikan pada hari H.
- Jelaskan berapa lama aksi bersih akan dilakukan, kapan waktu mulai dan waktu berakhir (biasanya aksi bersih berlangsung selama 1-2 jam)
- Jelaskan batas wilayah aksi bersih (di mana lokasi awal dan akhir)
- Jelaskan di mana lokasi akhir pengumpulan sampah dan jam berkumpul di lokasi akhir untuk pengambilan foto
- Pastikan agar relawan memisahkan sampah yang diambil sejak semula, hal ini lebih efisien jika dibanding dengan memisahkan kembali sampah yang dikumpulkan di akhir cleanup. Pemisahan jenis sampah akan mudah dilakukan jika Anda menugaskan para relawan untuk mengambil jenis sampah tertentu dan bergerak sebagai tim (misal, tim “pahlawan botol kaca,” atau tim “pahlawan botol PET”). Jika Anda hendak mengumpulkan data, Anda juga bisa menunjuk tim “pahlawan brand audit”
- Pastikan agar relawan tidak mengisi karung hingga terlalu penuh karena karung tersebut perlu diikat dan tertutup
- Tentukan siapa yang akan berada di titik akhir aksi bersih untuk menimbang sampah yang terkumpul dan melaporkan data.
- Tentukan siapa yang akan berjaga di titik awal untuk memberi penjelasan kepada relawan- relawan yang datang terlambat
- Tentukan siapa yang akan mengambil foto atau video selama aksi bersih. Informasikan pada mereka bahwa Anda akan mengambil foto atau video mereka: akan selalu lebih aman jika kita mengantungi ijin, dan Anda juga akan mendapat foto dan video yang lebih baik jika mereka siap untuk difoto.
Jadwal aksi bersih
Hadirlah di lokasi beberapa menit lebih awal untuk menunggu para relawan datang. Ambil beberapa foto lokasi sebelum aksi bersih. Bawalah bendera Trash Hero atau gunakan kaos kuning Trash Hero agar Anda gampang terlihat. Senyumlah dan sapa semua orang serta tunggu beberapa saat untuk relawan lain yang datang lebih akhir.
 Berikan penjelasan: Sambutlah semua orang yang hadir dan ucapkan terima kasih atas kehadiran mereka. Perkenalkan Trash Hero secara singkat dan jelaskan misi serta latar belakang singkat Trash Hero. Jelaskan rencana yang akan dilakukan pada hari tersebut (lihat poin sebelumnya). Ingatkan semua orang untuk bersenang-senang, beristirahat (jika perlu), minum air, dan percaya bahwa upaya mereka mengambil berapapun jumlah sampah akan sangat berharga.
Berikan penjelasan: Sambutlah semua orang yang hadir dan ucapkan terima kasih atas kehadiran mereka. Perkenalkan Trash Hero secara singkat dan jelaskan misi serta latar belakang singkat Trash Hero. Jelaskan rencana yang akan dilakukan pada hari tersebut (lihat poin sebelumnya). Ingatkan semua orang untuk bersenang-senang, beristirahat (jika perlu), minum air, dan percaya bahwa upaya mereka mengambil berapapun jumlah sampah akan sangat berharga.
Jika Anda memiliki kaos Trash Hero, sekarang adalah saatnya untuk menawarkan bahwa mereka dapat membeli kaos Trash Hero dengan harga biaya produksi, sehingga relawan bisa langsung memakainya selama aksi bersih. (Foto aksi bersih Anda akan terlihat lebih baik jika banyak orang yang menggunakan kaos Trash Hero)
Di akhir aksi bersih:
- Ambil beberapa foto setelah lokasi dibersihkan (di lokasi yang sama dengan foto sebelum lokasi dibersihkan)
- Ambil foto grup dan ambilah foto ceria dengan semua sampah yang dikumpulkan/li>
- Lakukan penutupan:
– Ucapkan terima kasih atas pertolongan mereka
– Ucapkan terima kasih kepada para sponsor dan sebutkan nama para sponsor
– Informasikan kepada semua orang berapa banyak sampah yang terkumpul dan ke mana sampah – dan data sampah – tersebut dikirim
– Jelaskan program Trash Hero lainnya yang sedang chapter Anda jalankan (misalnya program botol, tas, dll) dan informasikan bagaimana mereka dapat terlibat pada program-program tersebut
– Informasikan bahwa Anda akan memuat foto aksi bersih yang baru saja dilakukan di media sosial (mintalah ijin untuk melakukan hal tersebut) dan mintalah mereka untuk men-tag diri mereka masing-masing pada foto dan bagikan foto tersebut di profil mereka
- Kumpulkan alamat email relawan yang bersedia untuk terus terhubung dengan Trash Hero
- Rayakan bersama! (Sangatlah baik jika chapter Anda mendapat sponsor makanan, minum, atau hal lain yang dapat dinikmati bersama 17 setelah aksi bersih)
Setelah aksi bersih
Beristirahatlah! Lalu bersiap untuk membagikan kisah sukses Anda di media sosial. Usahakan untuk mempost foto kegiatan di hari yang sama, atau keesokan harinya, tergantung pada ketersediaan waktu dan tenaga Anda.
Daftar hal yang perlu dilakukan saat posting:
- Lihatlah satu per satu hasil foto Anda lalu pilihlah foto-foto terbaik (Anda juga bisa sedikit mengeditnya jika Anda bisa)
- Jejerkan foto lokasi sebelum dan sesudah aksi bersih dilakukan
- Buat album foto baru di laman facebook chapter Anda untuk setiap aksi bersih (Photos > Add Album)
- Tulislah judul album dengan format berikut: Nama chapter – nomor cleanup – tanggal – jumlah relawan – jumlah sampah yang dikumpulkan (dalam bahasa inggris). Contoh: “Trash Hero Batu Bolong :: Cleanup #27 :: 18.2.2018 :: 35 volunteers :: 215 kg”
- Beri informasi sebagai berikut pada bagian deskripsi:
 1. Tanggal aksi bersih
1. Tanggal aksi bersih
2. Lokasi aksi bersih
3. Berapa jumlah relawan yang bergabung. Jumlah ini mencakup jumlah relawan dewasa dan anak-anak. Lalu tulis juga jumlah anak-anak secara terpisah. Misalnya, terdapat 20 relawan dewasa dan 5 relawan anak-anak yang bergabung. Maka Anda perlu menulis: “25 relawan, termasuk 5 anak-anak.”
4. Berapa kilogram sampah yang terkumpul dan berapa banyak yang terkirim untuk di daur ulang (jika ada)
5. Ucapan terima kasih untuk sponsor yang berkontribusi di acara aksi bersih tersebut
6. Tambahkan kata penutup seperti “Kami melakukan aksi bersih sepeti ini setiap minggunya.” atau “Sampai bertemu lagi minggu depan!”
7. Tambahkan alamat website Trash Hero: trashhero.org
- Gunakan Facebook untuk melakukan “check in” di lokasi aksi bersih sehingga muncul tag lokasi pada Album secara otomatis
- Upload foto-foto pada album tersebut sesuai urutan yang Anda kehendaki
- Copy paste deskripsi album pada setiap foto, sehingga jika terdapat foto yang diunggah secara terpisah, kita bisa mengetahui aktivitas apa yang dilakukan di foto tersebut
- Tambahkan keterangan lain untuk foto yang bersangkutan di bawah deskripsi yang telah Anda copy paste
- Tag orang-orang yang Anda ketahui di foto- foto tersebut (jika bisa)
- Periksa sekali lagi, lalu publikasikan
Catatan: Anda bisa membagikan post dari chapter Anda dan mempost foto selfi Anda saat aksi bersih di akun Facebook pribadi Anda, tetapi jangan gunakan akun Facebook pribadi sebagai tempat utama Anda mempublikasikan aktivitas chapter Anda. Selalu gunakan laman (fan page) Facebook chapter Anda untuk melakukan publikasi, karena akan lebih mudah dicari oleh publik dan dapat dilihat oleh lebih banyak orang.
Jika Anda menyelenggarakan kegiatan aksi bersih yang cukup besar, atau acara spesial lainnya, Anda dapat menulis pesan pada Trash Hero Indonesia dan Trash Hero World sehingga kami dapat menjadikannya sebuat artikel di blog kami!
Anda juga akan perlu melaporkan data sampah dan relawan, jika Anda belum melakukannya pada saat aksi bersih. Silakan isi form pengisian data, yang tautannya bisa Anda pasang di ponsel maupun di aplikasi penjelajah internet Anda. Di video panduan ini Anda bisa mempelajari langkah-langkahnya. Sesekali waktu, cobalah untuk mengunggah foto sampul baru dengan foto grup baru beserta statistik pencapaian chapter Anda (jumlah aksi bersih, relawan, anak-anak, dan berat sampah yang terkumpul).
Ingatlah untuk menghitung jumlah relawan yang bergabung pada saat aksi bersih. Jika seorang relawan atau anggota tim Anda datang ke acara aksi bersih berulang kali, mereka dihitung sebagai satu orang setiap kali aksi bersih. Sebagai contoh, satu tim yang terdiri dari empat orang yang melakukan 10 aksi bersih akan dihitung sebagai “40 relawan” secara statistik.
Demikianlah informasi mengenai aksi bersih. Jika Anda bisa melakukan semua hal di atas, Anda hebat sekali! Beristirahatlah dan rayakanlah setiap momen tersebut dengan teman-teman dan pahlawan sampah lainnya. Ini adalah bagian yang sangat penting. Nikmatilah setiap prosesnya. Anda melakukan hal yang baik untuk dunia.
Setelah Anda selesai beristirahat, saatnya untuk memulai kembali. Rencanakanlah aksi bersih Anda selanjutnya, cucilah seluruh sarung tangan Anda, buatlah sebuah event di Facebook dan undanglah semua orang! Semakin sering Anda melakukannya maka akan terasa semakin mudah, percayalah.

Catatan: Ketika melakukan posting di media sosial, pastikan pesan yang dituliskan adalah pesan dan inspirasi positif. Anda ingin orang lain untuk memberikan tanggapan jempol dan hati, bukan wajah marah ataupun wajah sedih. Kita tidak diperkenankan menyalahkan dan mempermalukan orang-orang karena membuang sampah sembarangan (meskipun kita tahu siapa yang melakukannya). Kita adalah pahlawan sampah, bukan polisi sampah. Kita hanya perlu menyampaikan pesan tentang orang hebat yang melakukan pekerjaan hebat untuk lingkungan.
⬆ Kembali ke atas ⬆
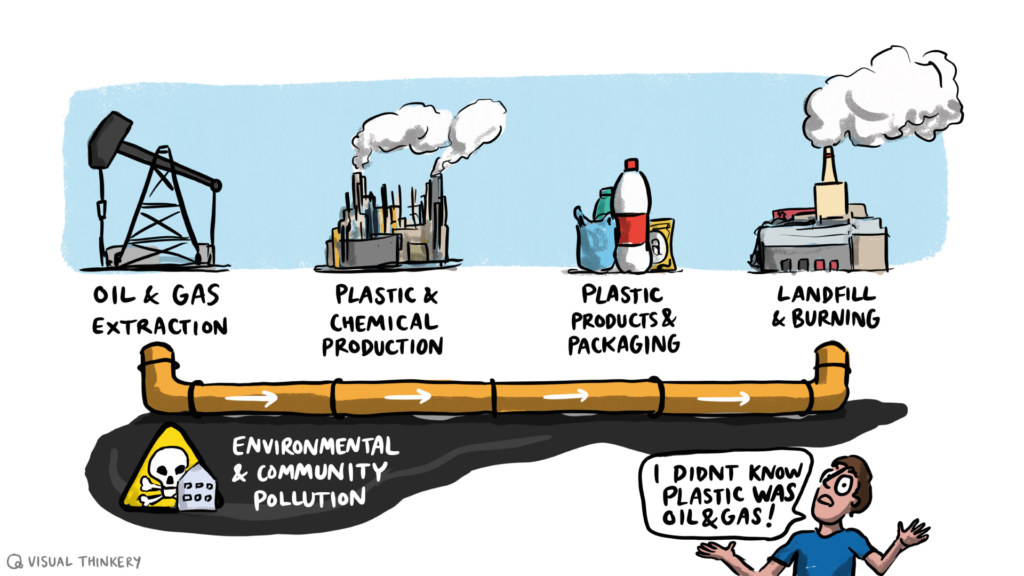
KEMANA SAMPAH DIANGKUT?
 Ini adalah pertanyaan yang hampir selalu ditanyakan oleh orang pada saat aksi berih. Jawabannya bergantung pada lokasi dan sistem pengelolaan sampah di lokasi tersebut.
Ini adalah pertanyaan yang hampir selalu ditanyakan oleh orang pada saat aksi berih. Jawabannya bergantung pada lokasi dan sistem pengelolaan sampah di lokasi tersebut.
Jika memungkinkan, pisahkan sampah yang dapat didaurulang dari total sampah yang terkumpul saat aksi bersih dan berikanlah sampah jenis ini pada perusahaan pendaurulang sampah profesional. Kertas bersih, kaca, dan logam sangatlah penting untuk didaur ulang karena bahan-bahan tersebut dapat didaur ulang secara terus-menerus tanpa penurunan kualitas yang berarti (“closed loop”). Daur ulang plastik biasanya bersifat “open loop” (menghasilkan bahan dengan kualitas lebih rendah dan sulit untuk dipakai ulang, yang akan dengan cepat berakhir di pembuangan akhir), tetapi kita tetap perlu melakukan itu sebagai usaha terakhir dari mengolah sampah yang kita kumpulkan.
Sejumlah sampah akan tetap berakhir di pembuangan akhir — hal ini menunjukan bahwa sampah tidak akan pernah “hilang”. Tujuan utama gerakan kita adalah mencegah terciptanya sampah sejak awal, sesuai dengan hirarki yang telah diterima secara umum yaitu:
1. KURANGI
2. GUNAKAN KEMBALI
3. DAUR ULANG
Program isi ulang botol Trash Hero adalah satu contoh dari bagaimana kita mencoba untuk mencapai tujuan ini. Program ini telah mengurangi timbulan sampah sebanyak 35 juta botol sekali pakai, sedangkan tas pakai ulang telah mengurangi jumlah sampah sebanyak lebih dari 9 juta kantong plastik sekali pakai.
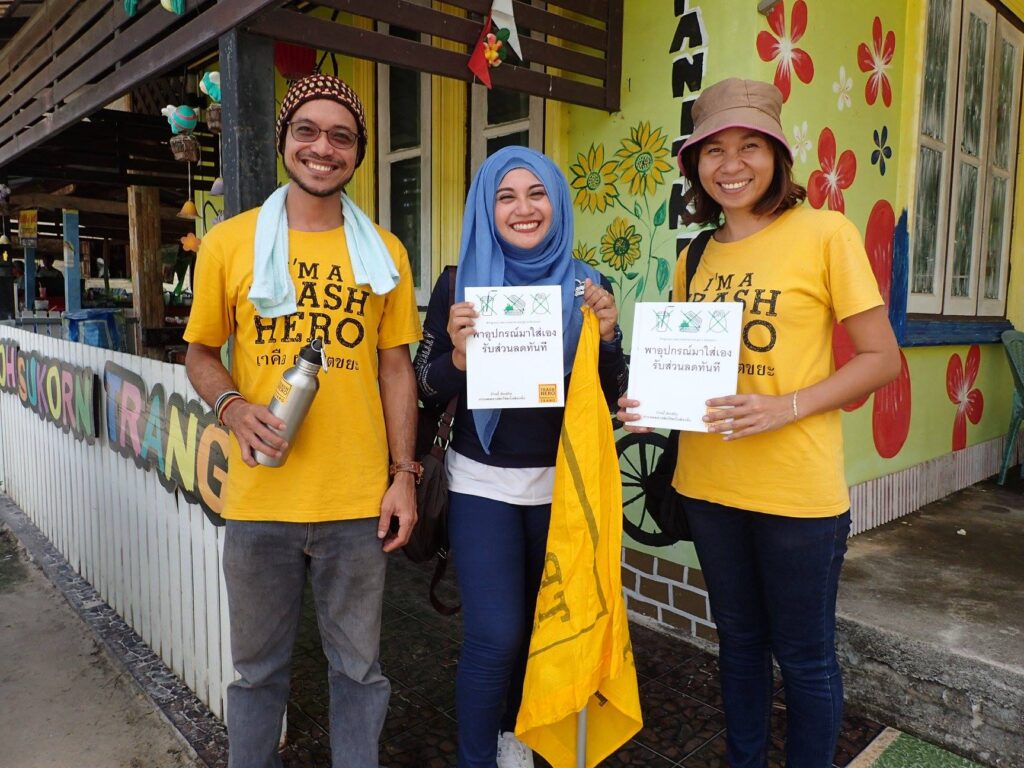
Beberapa chapter Trash Hero telah menciptakan beberapa program untuk mencegah munculnya sampah plastik. Trash Hero Ao Nang menyusun materi kampanye untuk mengurangi penggunaan sedotan plastik. Trash Hero Kertalangu dan Trash Hero Ende bekerja sama dengan sejumlah toko dan restoran di wilayah mereka untuk membantu mereka mulai menggunakan kantong plastik dan sedotan pakai ulang ketimbang yang berbahan plastik. Trash Hero Trang memulai skema diskon bagi pelanggan yang membawa tempat makan sendiri untuk pembelian makanan dan minuman bawa-pulang di kota mereka.
 APAKAH ANDA TAHU? Meski plastik PET dapat didaur ulang, jumlah botol PET di dunia yang mengandung bahan daur ulang hanya berkisar kurang dari 7%. Hal ini karena biasanya botol PET yang didaur ulang digunakan untuk membuat kain sintetis yang akan menjadi pakaian, karpet dan kemasan. Kain ini mencemari air setiap kali kita mencucinya, dan tidak dapat didaur ulang kembali dengan mudah, sehingga pada akhirnya akan berakhir di pembuangan atau kemungkinan lebih buruk lainnya. Beberapa botol PET yang berhasil didaur ulang menjadi kemasan lainnya hanya dapat kembali menjadi botol sebanyak maksimal empat kali, sebelum kualitasnya menurun dan akhirnya berakhir di TPA.
APAKAH ANDA TAHU? Meski plastik PET dapat didaur ulang, jumlah botol PET di dunia yang mengandung bahan daur ulang hanya berkisar kurang dari 7%. Hal ini karena biasanya botol PET yang didaur ulang digunakan untuk membuat kain sintetis yang akan menjadi pakaian, karpet dan kemasan. Kain ini mencemari air setiap kali kita mencucinya, dan tidak dapat didaur ulang kembali dengan mudah, sehingga pada akhirnya akan berakhir di pembuangan atau kemungkinan lebih buruk lainnya. Beberapa botol PET yang berhasil didaur ulang menjadi kemasan lainnya hanya dapat kembali menjadi botol sebanyak maksimal empat kali, sebelum kualitasnya menurun dan akhirnya berakhir di TPA.
Ke mana sampah diangkut? Tempat Pembuangan Akhir (TPA) vs. Pembakaran
Untuk menangani sampah yang sudah terlanjur ada, Trash Hero merekomendasikan opsi yang “terbaik dari yang terburuk” yang tersedia di sekitar. Opsi yang dimaksud adalah sesuatu yang berdampak paling kecil bagi kesehatan manusia dan kelestarian lingkungan. Di kebanyakan tempat, opsi ini berupa sistem pemisahan sampah yang dilanjutkan dengan pengomposan, pendaurulangan (jika memungkinkan), dan juga pembuangan di TPA.
Terdapat beberapa jenis tempat pembuangan sampah dan semuanya tidaklah ideal. Kami akan senantiasa mendorong pemerintah setempat untuk memperbaiki fasilitas-fasilitas ini jika diperlukan, ketimbang melakukan pembakaran.
Pembakaran plastik dalam bentuk apapun akan melepaskan emisi beracun dan menyia-nyiakan sumber daya yang masih bisa dimanfaatkan, sehingga kami tidak akan pernah menjadikan ini sebagai sebuah opsi. Sesi “Benar atau Salah?” akan menjelaskan lebih jauh. Singkatnya, tidak ada solusi yang sempurna untuk sampah yang sudah terlanjur ada: hal ini memperkuat alasan mengapa kita perlu memproduksi lebih sedikit sampah di masa depan.
⬆ Kembali ke atas ⬆
Benar atau salah?
Plastik saat ini dianggap sebagai masalah lingkungan dunia. Sebagai seorang Trash Hero, Anda mungkin akan memiliki berbagai ide untuk “menyelesaikan” permasalahan sampah. Tetapi yang manakah yang benar-benar bermanfaat dan yang manakah yang merupakan solusi palsu?

Apakah kita mengikuti jalan yang benar? Sebuah gambar yang mengejutkan dari GAIA
Dewasa ini seringkali muncul teknologi-teknologi dan produk-produk baru yang diperkenalkan sebagai “solusi” dari krisis plastik. Hal ini bisa memusingkan masyarakat, terutama jika mereka mengiklankannya dengan sangat baik.
Plastik dan tumbuhan! Bakteri pengurai plastik! Daur ulang kimia! Plastik jadi BBM! Terdapat lebih banyak lagi, tetapi inilah yang paling sering kita dengar.
Kita bisa menilai apakah ini solusi-solusi ini benar-benar bermanfaat dengan cara bertanya satu hal sederhana: apakah ini akan mengurangi sampah?
Dengan kata lain, apakah hal ini merupakan produk atau metoda yang membuat kita tetap berperilaku menghasilkan sampah, atau kah akan membuat kita menggunakan lebih sedikit plastik dan menghemat sumber daya alam dalam waktu panjang?
Kami percaya bahwa solusi mumpuni (solusi sesungguhnya) dari permasalah plastik adalah sesuatu yang bisa mengubah cara pembuatan, pendistribusian, dan penggunaan suatu bahan sehingga tidak dihasilkan sampah dalam bentuk apapun.
Program isi ulang botol Trash Hero adalah salah satu contoh solusi mumpuni. Sudah terdapat banyak solusi mumpuni lainnya, tetapi kita butuh lebih banyak solusi mumpuni, juga yang berskala global.
Solusi palsu tidak akan mengurangi sampah. Mereka hanya menawarkan cara alternatif pembuangan atau pemusnahan sampah. Biasanya mereka hanya menyelesaikan masalah secara sementara.
Simaklah beberapa ide yang sebelumnya telah disebutkan di atas dan periksa apakah mereka solusi mumpuni atau solusi palsu.
Insinerasi / Pembakaran
Terdapat banyak jenis mesin untuk membakar plastik atau sampah tercampur, yang menghasilkan energi atau bahan bakar untuk membantu penyediaan listrik dan transportasi. Mereka seringkali dianggap sebagai solusi yang baik atas permasalahan sampah plastik, terutama di lokasi yang tidak memiliki TPA. Seringkali dikatakan bahwa mereka lebih baik daripada TPA karena ada energi yang dihasilkan dari prosesnya.
 Tapi apa dampaknya? Banyak studi membuktikan bahwa pembakaran sampah, bahkan tanpa oksigen (yang dikenal sebagai “pirolisis”), tidaklah ramah lingkungan dan aman bagi kesehatan manusia. Pembakaran plastik melepaskan zat yang sangat beracun yang dapat memicu kanker, penyakit pernapasan, gangguan reproduksi, dan lainnya.
Tapi apa dampaknya? Banyak studi membuktikan bahwa pembakaran sampah, bahkan tanpa oksigen (yang dikenal sebagai “pirolisis”), tidaklah ramah lingkungan dan aman bagi kesehatan manusia. Pembakaran plastik melepaskan zat yang sangat beracun yang dapat memicu kanker, penyakit pernapasan, gangguan reproduksi, dan lainnya.
Bahkan mesin yang paling canggih sekalipun (yang biasanya ditemukan di negara-negara maju) tidak mampu menyaring semua dioksin dan logam berat berukuran nano yang dilepaskan dari proses pembakaran. Sehingga racun akan lepas ke udara bebas dan tanah di sekitar lokasi pembakaran. Dari sampah yang dibakar, hingga sekitar 20%-nya akan tersisa sebagai konsentrat abu beracun yang harus dibuang ke suatu tempat. Di bagian mana dari planet ini menurutmu tempat yang cocok untuk ini?
Selain membahayakan kesehatan, insinerator — atau plastik-menjadi-BBM, PLTSa, atau apapun istilahnya — tidak akan mengurangi jumlah sampah.
Data menunjukkan bahwa jumlah sampah di suatu kota cenderung meningkat setelah kota tersebut mulai menggunakan insinerator. Mesin ini harus beroperasi non-stop sehingga harus terus menerus diberi bahan bakar plastik. Sehingga akhirnya tidak ada motivasi untuk melarang plastik sekali pakai. Sampah juga akhirnya tidak perlu dipisah karena semua sampah bisa dibakar dengan mesin tersebut. Tingkat daur ulang akan menurut, yang artinya sumber daya yang masih bisa dimanfaatkan kembali akan terbakar dan hilang selamanya.
Insinerasi juga menyumbang percepatan perubahan iklim dan menghambat upaya menuju pemanfaatan energi surya, angin, maupun air.
Kesimpulan: SOLUSI PALSU
Bioplastik (PLA)
Terdapat banyak sekali jenis “plastik berbahan tumbuhan” yang terdengar alami dan ramah lingkungan. Mereka terbuat dari bahan organik seperti jagung atau singkong sebagai pengganti minyak bumi. Sebagian dari mereka berlabel “biodegradabel” dan “bisa dikompos” sehingga mereka banyak dipromosikan sebagai “alternatif plastik.”
 Jika kita teliti lebih lanjut label-label tersebut, seringkali bahan-bahan ini hanya bisa dikompos di fasilitas industri, di mana sampah bioplastik akan dipanaskan sampai 60C. Pada fasilitas ini bioplastik biasanya dipecah menjadi karbon dioksida dan air, sehingga tidak ada nutrisi tersisa yang bisa dijadikan kompos. Tidak ada studi yang menunjukkan apa yang akan terjadi pada zat kimia lain yang terdapat pada bioplastik tersebut. Zat-zat ini adalah zat-zat yang sama dengan plastik konvensional. Asam polilaktat atau PLA, jenis bioplastik yang umum diproduksi, telah diketahui mengandung jumlah racun yang sama-sama berbahayanya dengan PVC.
Jika kita teliti lebih lanjut label-label tersebut, seringkali bahan-bahan ini hanya bisa dikompos di fasilitas industri, di mana sampah bioplastik akan dipanaskan sampai 60C. Pada fasilitas ini bioplastik biasanya dipecah menjadi karbon dioksida dan air, sehingga tidak ada nutrisi tersisa yang bisa dijadikan kompos. Tidak ada studi yang menunjukkan apa yang akan terjadi pada zat kimia lain yang terdapat pada bioplastik tersebut. Zat-zat ini adalah zat-zat yang sama dengan plastik konvensional. Asam polilaktat atau PLA, jenis bioplastik yang umum diproduksi, telah diketahui mengandung jumlah racun yang sama-sama berbahayanya dengan PVC.
Jika tidak terdapat fasilitas pengomposan skala industri, maka sampah bioplastik akan dianggap sebagai sampah umum yang akan dikirim ke TPA atau dibakar. Jika dimasukkan ke fasilitas daur ulang, sampah bioplastik akan mengkontaminasi plastik-plastiknya dan membuat plastik-plastik tersebut tidak bisa digunakan kembali.
Tetapi apakah bioplastik benar-benar mengurangi sampah? Lagi-lagi, jawabannya adalah tidak. Bioplastik kebanyakan digunakan sebagai kemasan sekali pakai dan tidak dapat dimanfaatkan kembali setelah menjadi sampah. Mereka mensubstitusi plastik sekali pakai dengan bahan lain yang sedikit lebih baik, tetapi masih tetap sekali pakai.
Kesimpulan: SOLUSI PALSU
Daur Ulang Kimiawi
Mayoritas perusahaan yang menghasilkan produk makanan atau produk kebutuhan rumah tangga menyatakan bahwa tingkat daur ulang yang lebih tinggi adalah jawaban dari permasalahan sampah kemasan. Dengan begitu, mereka tidak perlu melakukan apapun! Mereka bisa terus memproduksi milyaran plastik sekali pakai setiap hari dan menyerahkan penanganan sampahnya pada konsumen atau sistem pengelolaan sampah di suatu lokasi.
Meskipun daur ulang memang membantu mengurangi sampah, tetap saja itu bukanlah solusi jangka panjang. Jumlah dan kualitas bahan akan berkurang setiap kali suatu bahan didaurulang. Dan setelah beberapa kali daur ulang, bahan tidak akan bisa digunakan lagi dan akhirnya menjadi sampah.

Proses pembuatan “Econyl,” poliester yang didaur ulang secara kimiawi yang diklaim sebagai “daur ulang tak terhingga.”
Saat ini terdapat daur ulang kimia. Ini adalah teknologi yang merupakan proses “repolimerisasi,” di mana plastik dipecah menjadi bentuk molekul asalnya lalu dibuat menjadi produk plastik baru secara “terus-menerus.” Hal ini disebut “plastik menjadi plastik (plastic-to-plastic).”
Walaupun ini bisa menjadi solusi yang potensial bagi plastik yang sudah terlanjur ada, teknologi ini sangatlah mahal. Mahalnya biaya proses ini membuatnya mustahil untuk bersaing dengan harga produksi plastik baru dari minyak bumi atau gas alam. Proses ini juga membutuhkan energi yang jauh lebih banyak, belum lagi racun dan limbah yang dihasilkan dari plastik awal.
Uni Eropa menyatakan bahwa teknologi repolimerisasi saat ini masih 10 tahun terlalu dini untuk bisa benar-benar diterapkan secara komersil — dan selama menunggu selama 10 tahun, produksi plastik baru akan terus bertambah.
Apakah ini akan mengurangi sampah? Saat ini, tidak. Secara teoritis, teknologi ini dapat memperpanjang umur suatu barang berbahan plastik. Tetapi kenyataannya – di skenario terbaik – hanya hanya sedikit sekali plastik yang bisa diperpanjang umurnya hingga 10 tahunan. Hal ini membuat teknologi jauh lebih tidak efektif dibanding pengurangan di sumber.
Kesimpulan: SOLUSI PALSU
Catatan: terkadang istilah “daur ulang kimiawi” digunakan untuk menjelaskan proses plastik-menjadi-BBM atau proses lainnya di mana dilakukan pembakaran (lihat “Insinerasi”). Proses ini memang bersifat “kimiawi,” tetapi yang jelas BUKAN merupakan “daur ulang.”
Nol sampah
Istilah “nol sampah” mencakup beberapa praktik yang dirancang untuk melindungi sumber daya alam yang terbatas, dan juga mencegah pembuangan apa pun. Praktik ini juga mencakup perubahan sistem secara keseluruhan, dimulai oleh produsen.
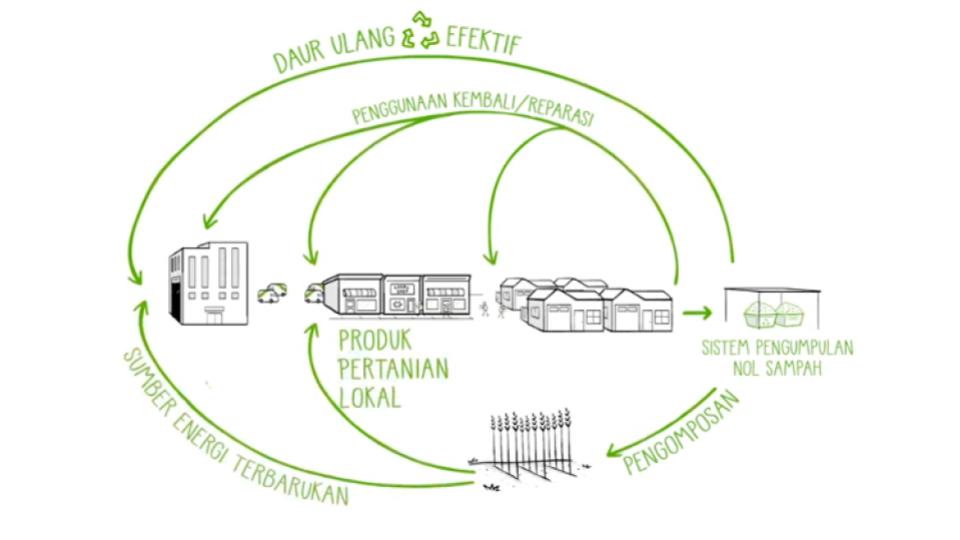
Produk didesain agar dapat digunakan kembali dan diisi ulang, serta diperbaiki atau diganti suku cadangnya. Bahan yang digunakan perlu dapat didaurulang secara mudah dan terus-menerus.
Pemerintah dapat berperan dalam memperkenalkan sistem pemisahan sampah. Sampah makanan dikompos; bahan lainnya dibersihkan lalu digunakan kembali atau didaur ulang secara lokal. Kita sebagai penduduk suatu wilayah dapat membantu pemerintah dan mendukung agar upaya ini berjalan secara efisien. Sampah yang muncul dengan jumlah sedikit dapat ditempatkan di TPA yang aman.
Apakah ini akan mengurangi sampah? YA! Nol sampah mungkin tidak dapat tercapai, tetapi ingatlah: plastik tidak digunakan secara umum 60 tahun lalu, dan kita bisa kembali ke gaya hidup tersebut namun dengan teknologi dan bahan-bahan yang lebih baik. Mengubah sistem mungkin untuk dilakukan dengan memanfaatkan momentum yang tepat, dan sebagai Trash Hero, ini adalah visi yang perlu kita capai.
Kesimpulan: SOLUSI MUMPUNI
Untuk mendapat informasi tambahan mengenai topik-topik ini, silakan periksa perpustakaan pengetahuan kami di trashhero.org/library!
⬆ Kembali ke atas ⬆
4. Menjalankan program botol minum isi ulang
Penjelasan program
Tujuan dari program ini adalah menawarkan solusi praktis dan terjangkau serta alternatif dari penggunaan plastik air minum sekali pakai dan untuk mengurangi jumlah botol plastik yang mencemari lingkungan.
 Program ini menyediakan botol minum stainless steel yang dijual kepada pelaku usaha lokal, untuk dijual kembali kepada pelanggan mereka dengan sedikit keuntungan. Jumlah keuntungan ini akan digunakan untuk menyediakan air minum isi ulang gratis kepada pelanggan yang memiliki botol minum Trash Hero, di manapun mereka membeli botol tersebut.
Program ini menyediakan botol minum stainless steel yang dijual kepada pelaku usaha lokal, untuk dijual kembali kepada pelanggan mereka dengan sedikit keuntungan. Jumlah keuntungan ini akan digunakan untuk menyediakan air minum isi ulang gratis kepada pelanggan yang memiliki botol minum Trash Hero, di manapun mereka membeli botol tersebut.
Program ini akan sangat bergantung pada dukungan dari komunitas lokal. Mitra kerja sama dapat berupa hotel, kafe, toko, bar, operator selam, atau tempat non-komersil seperti ruang kumpul komunitas. Semakin banyak mitra kerja sama yang bergabung dalam program ini, akan semakin besar jaringan isi ulang air minum yang ada di lokasi tersebut.
Untuk bergabung dalam program ini, pelaku usaha perlu menyetujui ketiga komitmen di bawah ini:
- Menjual botol dengan harga jual tetap yang ditentukan kepada semua konsumen (sebagai contoh, di Indonesia harga botol adalah Rp130,000)
- Menyediakan isi ulang air layak minum gratis bagi semua pemilik botol Trash Hero. Papan petunjuk isi ulang harus terlihat dan dapat diakses dengan mudah oleh semua konsumen.
- Meletakkan poster program yang telah didesain oleh Trash Hero.
Mengenai botol Trash Hero
Botol Trash Hero terbuat dari stainless steel 304 yang aman untuk mengemas makanan. Dinding botol tidak memakai insulasi dan dapat menampung cairan dengan hingga 750ml.
 Saat ini barang diimpor dari Cina, dan kami masih mencari produsen lokal. Trash Hero memiliki sertifikat mengenai kualitas dan komposisi bahan menyusun botol tersebut untuk ditunjukkan kepada pada pelaku usaha dan pelanggan mereka.
Saat ini barang diimpor dari Cina, dan kami masih mencari produsen lokal. Trash Hero memiliki sertifikat mengenai kualitas dan komposisi bahan menyusun botol tersebut untuk ditunjukkan kepada pada pelaku usaha dan pelanggan mereka.
Seluruh botol memiliki logo Trash Hero di bagian depan, bersama dengan tulisan “Love” dan nama negara Anda (contoh: “Love Indonesia”) atau “Love” dan nama lokasi (contoh: “Love Flores”).
Botol bisa juga dilengkapi dengan logo usaha maupun logo sponsor di bagian belakang — untuk order khusus seperti ini, silakan baca informasi di bawah ini.
Memulai program botol
Jika Anda ingin memulai program botol, langkah pertama yang perlu dilakukan adalah menghubungi chapter Trash Hero lain di negara Anda yang telah memulai program ini. Mereka dapat berbagi pengalaman dan membantu Anda mendapat sampel botol. Jika Anda chapter pertama yang memulai di negara Anda, kontaklah tim mentor di negara Anda.
Mencari mitra
Selanjutnya, Anda perlu mulai membangun jaringan isi ulang air minum. Hal termudah untuk memulainya adalah dengan mendekati tempat yang biasa Anda kunjungi atau Anda kenal dengan pemiliknya. Jika tim Anda tidak memiliki koneksi dengan mitra yang potensial, mintalah rekomendasi pada jejaring sosial Anda atau datangi tempat yang memiliki nilai dan misi yang serupa dengan Trash Hero, misalnya, toko produk ramah lingkungan, eco resort, green café, atau tempat kursus yoga.
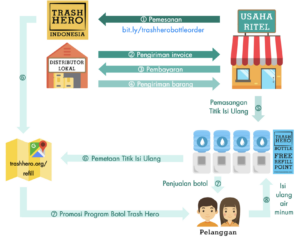
Jelaskan tujuan dari program ini, dan pastikan mereka mengerti bahwa Trash Hero bukanlah sebuah perusahaan dan chapter Trash Hero maupun para relawan tidak mendapat keuntungan sepeser pun. Bersabarlah dan jangan memaksa mereka untuk bergabung.
Kami memiliki materi yang mencakup seluruh informasi mengenai program botol yang dapat diunduh. Beberapa poin inti yang harus dikomunikasikan saat memperkenalkan program botol ini adalah:
- Program ini mudah untuk dicoba: Anda bisa memulai dengan jumlah kecil.
- Program ini membantu penjualan: meski mereka tidak membuat keuntungan yang besar dari penjualan botol, banyak tempat usaha yang melaporkan terjadinya peningkatan penjualan karena orang membeli hal lain ketika mereka mengisi ulang air minum. Tidak ada partner yang pernah melaporkan kerugian dengan bergabung dalam program ini.
- Program ini etis: tidak hanya baik bagi lingkungan, namun program ini juga baik bagi masyarakat. Ini adalah cara termudah bagi mereka untuk menunjukkan kepedulian terhadap lingkungan.
- Program ini dapat dimanfaatkan sebagai iklan gratis: semua mitra akan mendapat ucapan terima kasih pada halaman Facebook dan mendapatkan link khusus di website Trash Hero, juga terdaftar pada peta isi ulang Trash Hero yang dapat diakses oleh publik secara online. Mitra juga dapat meletakkan stiker mereka pada botol yang mereka jual, atau membuat grafir logo di bagian belakang (terdapat jumlah pemesanan minimum order untuk pembuatan grafir logo ini).
- Program ini dapat dimanfaatkan sebagai strategi marketing: saat ini semakin banyak konsumen yang menghargai bisnis yang memiliki program ramah lingkungan. Banyak orang akan memilih tempat makan atau berbelanja yang memiliki program semacam ini, dan mereka akan menyebarkannya kepada teman atau melalui jejaring media sosial mereka.
Pemesanan pertama Anda
Botol akan dikemas dalam dus satuan. Pemesanan minimum adalah 20 botol, sedangkan untuk partai besar, pemesanan harus dilakukan per kelipatan 50. Semua pesanan harus dibayar di muka.
Stok botol akan diatur oleh team Trash Hero Indonesia; silakan kontak pengurus Trash Hero Indonesia untuk mengetahui jumlah stok botol yang tersedia dan melakukan pemesanan.
Botol-botol ini memiliki desain “Love [nama negara]”. Jika Anda ingin memesan botol dengan desain “Love [nama lokasi]” atau memesan logo perusahan untuk digrafir di bagian belakang, silakan lakukan pemesanan khusus, di mana Anda perlu memesan dengan jumlah minimum tertentu. Misalnya di Indonesia, minimum order untuk botol dengan desain khusus adalah khusus adalah 50 buah. Anda perlu mengumpulkan pesanan yang cukup banyak agar memiliki cukup dana untuk melakukan pemesanan khusus ini.
Pada kasus-kasus di mana Anda mendapatkan botol yang rusak setelah pengiriman, silakan ambil foto dari botol tersebut dan hubungi pemasok Anda.
Penyimpanan dan distribusi
Beri tugas kepada salah satu orang dari tim Anda untuk bertanggungjawab dalam pemeriksaan dan update stok botol di chapter Anda, serta menjadi kontak untuk pemesanan baru.
Di awal program dan saat jumlah stok masih sedikit, anggota tim dapat menaruh persediaan botol ini di rumah mereka.
Namun ketika jumlah stok menjadi lebih besar, Anda mungkin perlu mencari orang atau bisnis yang bersedia menampung dus-dus botol tersebut secara gratis. Tempat penyimpanan haruslah kering dan jauh dari udara laut yang mengandung garam, dan ditangani oleh orang yang dapat Anda percaya. Tentu saja setiap orang yang menawarkan bantuan ini perlu diapresiasi dengan ucapan terima kasih melalui Facebook, sama halnya dengan setiap mitra baru pada program isi ulang air minum.
Pastikan untuk hanya kirimkan botol pada mitra setelah tempat isi ulang mereka siap dan poster telah dipasang di tempat mereka. Cara pemeliharaan botol juga perlu dijelaskan kepada mereka. Jika tempat usaha terletak dekat dengan laut, maka mereka sebaiknya menaruh hanya satu sampel sebagai contoh, sisanya harus ditaruh di dalam kotak agar terlindung dari udara laut.
Pelanggan mereka harus diingatkan untuk:
- mencuci botol secara berkala dengan tangan, botol ini tidak diperuntukkan untuk dicuci di
mesin pencuci piring
- mencucinya dengan air bersih secepatnya setelah digunakan di laut atau pantai
- isilah hanya dengan minuman dingin (botol ini tidak didesain untuk air panas)
Dengan perawatan yang benar, botol ini akan bertahan seumur hidup.
Cara promosi dan perluasan jaringan
Materi promosi cetak
Trash Hero akan menyediakan tiga poster untuk mitra. Dua poster cetak berisi informasi umum: satu poster berisi iklan isi ulang air minum, yang akan diletakkan di luar bangunan usaha; dan satu poster khusus bagi hotel yang menaruh botol di kamar-kamar mereka sebagai pengganti air minum dalam kemasan plastik seperti yang diberlakukan di hotel pada umumnya. Dokumen-dokumen untuk poster ini dapat dikirim secara digital untuk dicetak secara mandiri. Simpan tanda bukti dan ambil foto poster yang sudah dipasang agar Trash Hero dapat mengganti biaya yang dikeluarkan.
 Media sosial
Media sosial
Buatlah sebuah post Facebook untuk menyambut dan berterimakasih kepada mitra baru dengan sebuah foto botol di tempat usaha mereka, beserta pemilik bisnis atau dengan seorang konsumen. Foto ini harus diletakkan di album terpisah yang menunjukan semua mitra isi ulang air minum. Tag masing-masing usaha yang bekerjasama dan lakukan “check in” di lokasi tersebut.
Perluas jejaring isi ulang dengan mem-post informasi tentang program botol Trash Hero dan alasan mengapa kita melakukan ini di grup-grup Facebook dan di laman Facebook.
Tatap muka
Jika Anda menjalankan program aksi bersih, selipkan informasi mengenai program botol saat Anda menjelaskan tentang aksi bersih, atau tunjukan bahwa tim Anda menggunakan botol Trash Hero di hari tersebut. Anda juga dapat merencanakan pertemuan informal dengan calon mitra dan mengundang beberapa mitra yang telah bergabung untuk menjelaskan bagaimana program ini berimbas pada usaha mereka.
Penjualan botol melalui chapter
Jika seseorang menghubungi Anda di sebuah aksi bersih atau di mana pun, dan berminat untuk membeli botol, arahkan mereka untuk membeli botol di salah satu mitra Anda. Jangan menjual botol secara pribadi atau melalui chapter, kecuali ada kegiatan khusus (seperti konferensi atau festival) dimana Trash Hero menyediakan isi ulang air minum gratis.
Dalam kasus ini, botol harus dijual dengan harga pokok, karena isi ulang air minum biasanya disediakan oleh sponsor atau penyelenggara acara.
Peta jejaring isi ulang air minum
Semua mitra akan disertakan dalam peta global jejaring isi ulang air minum Trash Hero: trashhero.org/refill Silakan hubungi map@trashhero.org untuk mendaftarkan mitra baru Anda. Sangatlah penting untuk tetap memperbarui peta setiap kali ada mitra baru yang bergabung. Gerai-gerai usaha ini akan mendapat tanda kuning di peta.
Gerai-gerai usaha juga dimungkinkan untuk menyediakan air minum isi ulang tanpa menjual botol Trash Hero. Mereka akan mendapat tanda biru di peta. Dengan fleksibilitas ini mereka dapat tetap mempromosikan jasa ramah lingkungan mereka dan kita dapat memperluas jejaring di mana pemilik botol Trash Hero dalam melakukan isi ulang.
Gerai usaha dapat mendaftarkan diri melalui situs web dan perlu menyediakan foto titik isi ulang di gerai usaha masing-masing yang telah dibuat sebelumnya. Tentu saja akan lebih baik jika mereka menjual botol dan menyediakan air minum isi ulang.
⬆ Kembali ke atas ⬆
5. Mempersiapkan program tas pakai ulang
Program tas pakai ulang ini kurang lebih sama dengan program botol. Keduanya memiliki tujuan yang sama yaitu untuk mengurangi penggunaan plastik sekali pakai melalui strategi yang sama, yaitu menyediakan produk untuk dijual oleh bisnis lokal dengan harga pokok, untuk mereka jual kepada pelanggan mereka dengan sedikit keuntungan.
 Mengenai tas pakai ulang Trash Hero
Mengenai tas pakai ulang Trash Hero
Tas pakai ulang Trash Hero memiliki warna kuning, dengan logo Trash Hero di bagian luarnya, dan merupakan produk buatan tangan yang diproduksi di Indonesia. Tas ini terbuat dari hasil daur ulang botol PET. Tas ini berukuran 35cm x 40cm, dan setelah dilipat menjadi kantong kecil akan berukuran 10cm x 10cm dengan pengait logam.
Mengenai program tas Trash Hero
Tas ini dijual dengan harga pokok kepada mitra yang dapat menjualnya kembali atau memberikannya secara cuma-cuma kepada pelanggan mereka sebagai pengganti kantong plastik sekali pakai. Beberapa hotel dapat menggunakannya sebagai gantungan kunci agar setiap tamu dapat menggunakan tas ini selama mereka tinggal di hotel. Tas ini juga terlihat cocok disandingkan dengan botol Trash Hero: tas dapat dikaitkan di tutup botol dan dapat dijual sebagai paket “eco-package” untuk mengurangi sampah.
 Cara melakukan pemesanan
Cara melakukan pemesanan
Pertama-tama, cobalah hubungi tim mentor Anda: di negara Anda mungkin terdapat persediaan tas. Jika dibutuhkan pemesanan baru, biasanya terdapat jumlah minimum pemesanan yang akan mereka informasikan kepada Anda. Anda dapat membagi jumlah ini dengan chapter lain yang lokasinya dekat, atau dengan mendapatkan sponsor. Untuk bisnis yang memesan dalam jumlah besar, mereka dapat mencetak logo usaha mereka di bagian belakang tas.
Untuk informasi lebih lanjut, Anda bisa menghubungi bag@trashhero.org
⬆ Kembali ke atas ⬆
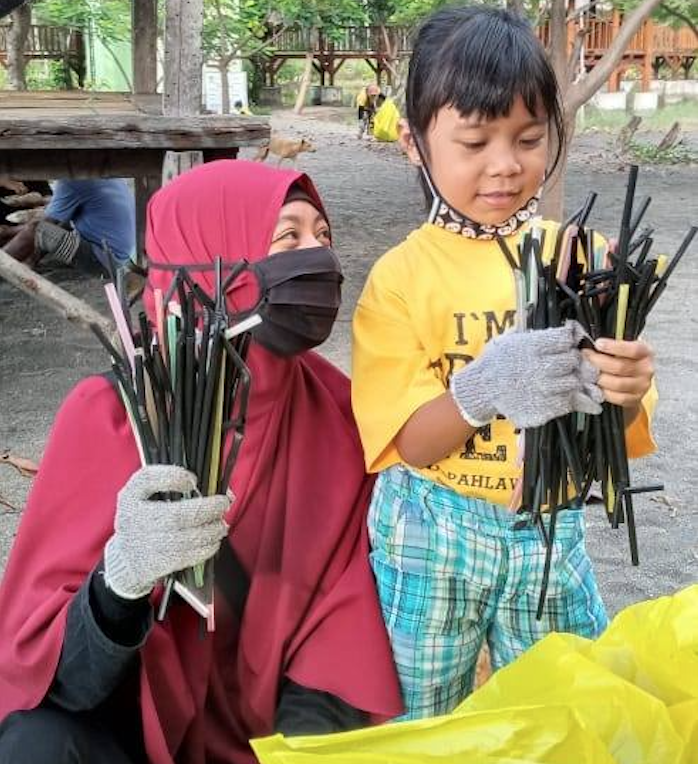
6. Melibatkan anak-anak
 Anak anak, remaja, dan keluarga mereka adalah bagian penting dalam gerakan ini. Kita memiliki materi pendidikan untuk umum serta program yang didesain khusus untuk anak-anak di mana chapter dapat menjalankannya dengan melibatkan anak-anak di lingkungan sekitar.
Anak anak, remaja, dan keluarga mereka adalah bagian penting dalam gerakan ini. Kita memiliki materi pendidikan untuk umum serta program yang didesain khusus untuk anak-anak di mana chapter dapat menjalankannya dengan melibatkan anak-anak di lingkungan sekitar.
Menjaga keamanan anak-anak
Sangat penting untuk memastikan anak-anak yang berpartisipasi di kegiatan Trash Hero untuk tetap sehat dan terjaga keamanannya. Seluruh chapter harus membaca dan setuju dengan kebijakan yang dibuat Trash Hero terkait perlindungan anak.
Materi edukasi
Terdapat bagian khusus di website Trash Hero mengenai anak-anak. Bagian ini ditujukan untuk anak berumur 8-10 tahun, tetapi juga cocok untuk anak yang berusia lebih muda dengan bantuan orang dewasa untuk membaca. Anda akan menemukan informasi, video, dan quiz untuk membuat anak-anak tertarik membahas masalah-masalah lingkungan, juga foto dan program anak-anak Trash Hero lainnya di seluruh dunia sebagai bahan inspirasi.Jika Anda memiliki cerita atau foto dari chapter Anda untuk ditambahkan di sini, silakan kirim pesan ke kids@trashhero.org.
Kami juga menyediakan poster dalam berbagai bahasa untuk di download dan di cetak.
Program Trash Hero Kids
Kami memulai “Trash Hero Kids” pada tahun 2018, setelah melihat banyaknya anak-anak yang senang turut serta pada aksi bersih kami dan menjadi seorang pahlawan. Program ini merupakan program jangka panjang yang terstruktur untuk membantu anak-anak usia 5 hingga 10 tahun memahami masalah sampah dan menjalankan praktik-praktik ramah lingkungan di kehidupan sehari-hari. Seperti kegiatan Trash Hero lainnya, proses belajar didesain agar ringan, positif, dan mudah dibawakan.
Inti dari program ini adalah buku yang didesain khusus untuk anak-anak. Buku ini tersedia dalam beberapa bahasa, termasuk Bahasa Inggris, Jerman, Ceko, Thailand, Indonesia, dan Malaysia.
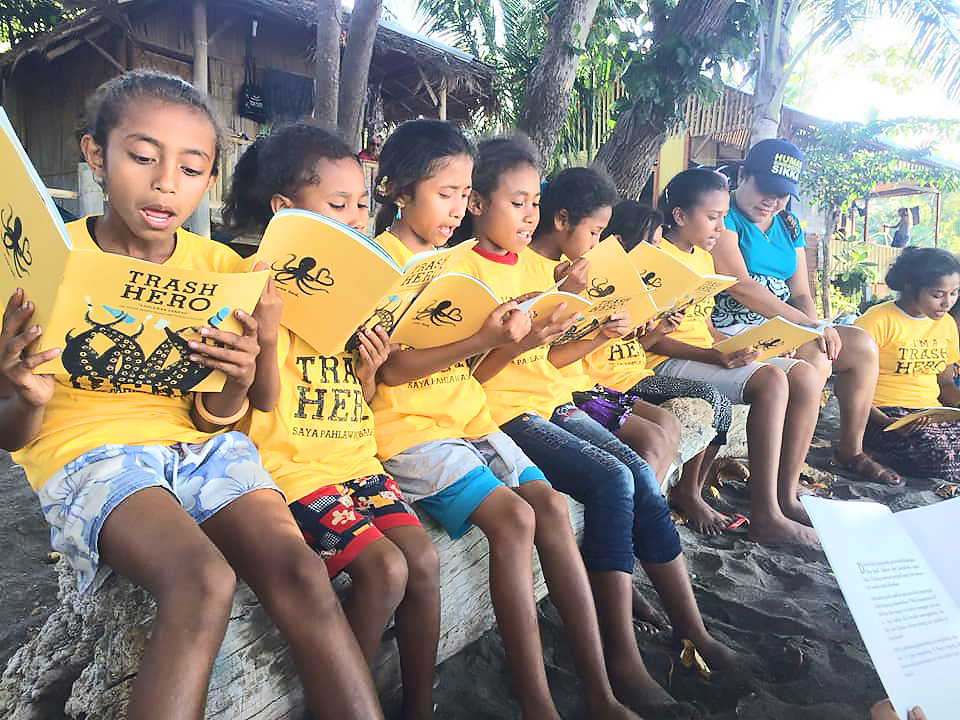

Buku ini diawali dengan sebuah cerita tentang seorang anak bernama Trash Hero, yang memperkenalkan isu pencemaran sampah dan plastik secara sederhana dan mudah dipahami anak-anak. Cerita ini menjelaskan bagaimana perialku kita sehari-hari memberi dampak negatif bagi lingkungan, dan bahwa setiap anak memiliki kekuatan untuk mengubah situasi ini.
Selain cerita tersebut, terdapat juga kumpulan fakta dan informasi tentang plastik di lautan dan apa yang terjadi dengan sampah yang kita buang. Kumpulan fakta dan informasi ini dapat memberi pemahaman yang bisa menjadi dasar diskusi berbagai aspek terkait pencemaran dan “3R” (Reduce, Reuse, Recycle – Mengurangi, Menggunakan Kembali, Daur Ulang.)
Di bagian akhir terdapat beberapa tantangan bagi anak-anak untuk melakukan aksi dan menjadi Trash Hero secara mandiri. Terdapat 7 kegiatan yang dapat dilakukan berulang kali untuk menciptakan sebuah kebiasaan baru. Setiap kali mereka menyelesainkan sebuah kegiatan, mereka perlu mencatatnya dan mengumpulkan poin untuk mendapatkan penghargaan berupa kaos Trash Hero dan sertifikat.
Program ini dapat dijalankan dengan dua cara: oleh chapter kita dengan anak-anak yang datang secara rutin; atau melalui kerja sama dengan sekolah atau komunitas lokal di mana seorang guru dapat berkomitmen minimal satu jam per minggu untuk membawakan suatu topik. Program ini tidak didesain untuk satu kali tatap muka*.
Kami menyediakan tata cara bagi para guru dalam Bahasa Indonesia. Terkadang terdapat mentor di yang dapat membantu menyediakan materi edukasi. Jika Anda memiliki cukup waktu, Anda mungkin perlu mencoba untuk membawakan sesi presentasi edukasi di sekolah. Atau Anda juga bisa melibatkan anak-anak di aksi bersih chapter Anda, yang mana itu juga merupakan salah satu kegiatan yang mereka bisa catat di buku mereka.
Program ini adalah salah satu kegiatan yang paling bermanfaat yang bisa Anda lakukan sebagai seorang relawan, namun juga menuntut komitmen waktu yang cukup besar untuk mengorganisir dan mengembangkannya. Anda perlu melakukan pelaporan tambahan, sebagai mana Trash Hero perlu menyediakan bahan-bahan ajar yang diperlukan yaitu buku, kaos, dan sertifikat, secara gratis. Harap untuk menimbang dengan seksama apakah Anda bisa menjalankan komitmen ini sebelum memulai program ini untuk menghindari kekecewaan anak-anak di kemudian hari.
Program ini hanya diperbolehkan untuk dilakukan oleh chapter yang sudah memiliki logo kuning. Silakan hubungi Country Coordinator atau email kids@trashhero.org untuk mendapat informasi lebih lengkap.
*Untuk kegiatan satu kali tatap muka dan presentasi yang melibatkan anak-anak, kami memiliki buku serupa dalam versi PDF di situs kami. Hampir semua kegiatan tantangan dapat diadaptasikan dengan kondisi wilayah masing-masing, dan sejumlah chapter telah berhasil membimbing anak-anak melakukan pementasan atas cerita ini sebagai bagian dari kegiatan tantangan.
⬆ Kembali ke atas ⬆
7. Menjangkau masyarakat secara lebih luas
Permasalahan terkait sampah hanya dapat diselesaikan secara mumpuni jika Anda mampu merangkul masyarakat dan menginspirasi mereka untuk melakukan perubahan. Masyarakat perlu merasa bahwa mereka adalah bagian dari Trash Hero dan melihat misi Trash Hero sebagai misi pribadi mereka juga. Berikut adalah beberapa ide untuk mencapai tujuan ini:
Bekerja sama dengan komunitas pebisnis lokal
 Seringkali terdapat acara yang diselenggarakan oleh perkumpulan hotel atau pebisnis di mana Anda dapat mempresentasikan dan menjelaskan tentang bagaimana perusahaan dapat ambil bagian dalam melakukan aksi. Tanyakan apakah mereka akan memperkenalkan Trash Hero kepada para anggota mereka dan mengirim karyawan mereka pada acara aksi bersih mingguan, atau mungkin memberi bantuan jasa pada chapter Anda.
Seringkali terdapat acara yang diselenggarakan oleh perkumpulan hotel atau pebisnis di mana Anda dapat mempresentasikan dan menjelaskan tentang bagaimana perusahaan dapat ambil bagian dalam melakukan aksi. Tanyakan apakah mereka akan memperkenalkan Trash Hero kepada para anggota mereka dan mengirim karyawan mereka pada acara aksi bersih mingguan, atau mungkin memberi bantuan jasa pada chapter Anda.
Anda bisa mendekati perusahaan yang lebih besar secara langsung: mereka biasanya memiliki program wajib CSR dan mereka akan menyambut dengan senang kesempatan untuk berpartisipasi di program Anda.
Beri motivasi pada perusahaan untuk menjadi contoh bagi perusahaan-perusahaan lain sejenis, dan apresiasi mereka sebagai pahlawan lokal dengan mengumumkan keterlibatan mereka di sosial media. Sebagai contoh, jika sebuah restoran berhenti menggunakan sedotan plastik atau memberikan diskon bagi konsumen yang datang dengan gelas sendiri, umumkan hal ini di Facebook sehingga bisnis lain dapat terinspirasi untuk meniru langkah mereka.
Buatlah grup chat tertutup (Line, WhatsApp, Messenger, atau apapun yang sesuai di lokasi Anda) dengan para pemilik bisnis dan sponsor yang tertarik untuk bergabung dengan program Anda. Informasikan kepada mereka secara berkala tentang kegiatan-kegiatan yang Anda lakukan. Grup chat ini juga dapat menjadi wadah bagi Anda untuk meminta dukungan.
Pimpin dan buat sebuah pertemuan atau workshop di tempat yang netral di mana semua orang dapat hadir untuk bergabung dan berdiskusi tentang “bagaimana cara membuat lingkungan kita lebih bersih.” Jangan anaktirikan siapapun, tetaplah mandiri dan netral tanpa memihak sisi manapun, dan jangan terasosiasi dengan salah satu bisnis atau rantai bisnis apapun. Sangat penting untuk membangun sebuah jaringan sponsor dan pendukung yang luas dan beragam.
Beberapa bisnis bisa saja ingin memberikan dukungan yang lebih besar dari yang dibutuhkan. Berpikir kreatiflah dan carilah jalan untuk menerima dukungan tersebut. Sebuah resort bisa saja memesan 100 kaos Trash Hero untuk dibagikan secara gratis, atau sebuah spa dapat menawarkan satu voucher gratis pada setiap minggu bagi relawan yang hadir di aksi bersih — Anda bisa memberi hadiah doorprize setelah aksi bersih berakhir. Selama tidak ada uang yang terlibat, tidak ada masalah untuk memberikan hadiah kepada relawan.
“Bangunlah jejaring pendukung yang besar dan luas”
Bekerja sama dengan organisasi-organisasi pejuang lingkungan lainnya
 Berkolaborasilah dengan organisasi swadaya lainnya atau di kegiatan peduli lingkungan di lingkunganmu atau kegiatan global. Kita tidak berkompetisi dengan siapapun: hanya dengan bekerja bersamalah kita dapat membuat perubahan.
Berkolaborasilah dengan organisasi swadaya lainnya atau di kegiatan peduli lingkungan di lingkunganmu atau kegiatan global. Kita tidak berkompetisi dengan siapapun: hanya dengan bekerja bersamalah kita dapat membuat perubahan.
Contoh:
– Melakukan brand audit pada aksi bersih chapter Anda dan menyediakan data bagi organisasi seperti Break Free From Plastic.
– Buatlah acara bersama atau setidaknya atur agar kegiatan aksi bersih Anda tidak dilakukan di hari yang sama atau di tempat yang sama dengan organisasi lain.
Bekerjasama dengan instansi pemerintah
Perkenalkan chapter Trash Hero Anda pada beberapa instansi pemerintah dan ajaklah mereka untuk bergabung di kegiatan Anda. Pastikan mereka mengerti bahwa Trash Hero tidak akan membuat publikasi negatif atau menyalahkan pihak manapun. Kita juga tidak menunjukkan bahwa lokasi aksi bersih kita adalah lokasi yang buruk; kita hanya menunjukkan bahwa terdapat sekelompok orang yang melakukan aksi bersih bersama. Kita di sini untuk membantu. Jangan pernah terlibat di politik lokal.
 Jika Anda memiliki hubungan baik dengan pemerintah lokal, Anda dapat memperbaiki kondisi lingkungan di wilayah Anda dengan memperkenalkan masyarakat dengan orang yang tepat untuk berdiskusi dan menerapkan solusi, misalnya dengan menyediakan lebih banyak tempat sampah untuk masyarakat umum. Pelaku usaha dapat memberi sponsor dengan cara menyediakan barang dan membayar pegawai untuk mengangkut sampah, dengan timbal balik berupa penulisan logo usaha di tempat sampah tersebut.
Jika Anda memiliki hubungan baik dengan pemerintah lokal, Anda dapat memperbaiki kondisi lingkungan di wilayah Anda dengan memperkenalkan masyarakat dengan orang yang tepat untuk berdiskusi dan menerapkan solusi, misalnya dengan menyediakan lebih banyak tempat sampah untuk masyarakat umum. Pelaku usaha dapat memberi sponsor dengan cara menyediakan barang dan membayar pegawai untuk mengangkut sampah, dengan timbal balik berupa penulisan logo usaha di tempat sampah tersebut.
Atau, Anda bisa mencari seniman lokal atau murid sekolah untuk mengecat atau mendesain tempat sampah, dan pemerintah bertugas mengangkut sampah secara berkala. Yang terpenting adalah bagaimana membuat semua proses ini transparan dan apabila melibatkan sejumlah uang, maka semua hal harus diumumkan di media sosial dan diumumkan kepada masyarakat untuk membuktikan bahwa Trash Hero tidak mendapat keuntungan finansial. Selalu ingat untuk mengungkapkan ide Anda dalam bentuk positif, dan tidak menunjukan rasa marah atau menyalahkan orang lain apabila ide tersebut tidak direalisasikan. Bekerja dengan pemerintah biasanya memakan banyak waktu, dan ini adalah sesuatu yang normal.
Libatkan tim Anda di festival lokal: beri saran pada penyelenggara untuk menjadikan acara tersebut nol sampah atau sediakan lebih banyak tempat sampah di tempat acara berlangsung. Bantu mereka untuk merencanakan sebuah aksi bersih dengan para pegawai mereka setelah acara berlangsung dan pastikan mereka berkomitmen untuk memperbaiki sistem pengelolaan sampah mereka selama festival.
Tolong pahami bahwa setiap kolaborasi membutuhkan kerja sama tim. Selalu ada kemungkinan di mana orang meminta tim Anda untuk membersihkan suatu tempat — ini bukanlah kerja sama! Kerja sama berarti bekerja bersama: misalkan sebuah bisnis menyediakan relawan atau sumber daya lain untuk melakukan aksi bersih dan setuju untuk menyediakan tempat sampah setelah wilayah tersebut dibersihkan. Sangatlah penting untuk diingat bahwa Trash Hero bukanlah petugas kebersihan.
⬆ Kembali ke atas ⬆
8. Menggunakan media sosial & media konvensional
Mengapa menggunakan media sosial?
Media sosial adalah cara paling penting bagi chapter Anda berkomunikasi dengan pihak luar. Laman Facebook chapter Anda adalah “citra” publik dan “suara” Anda. Anda mengendalikan apa yang Anda posting dan bagaimana chapter Anda terlihat oleh publik.

Hal tersebut berperan untuk:
MELIBATKAN
– menunjukkan kepada masyarakat lokal tentang apa yang Anda lakukan dan memberikan apresiasi kepada mitra, sponsor atau organisasi lain yang bekerjasama dengan Anda
– menjadi jembatan penghubung antar masyarakat, terutama jika posting dibuat dalam dua bahasa
– terhubung dengan orang-orang dan berbagi informasi
MENGINSPIRASI
– menunjukkan bahwa Anda adalah bagian dari masyarakat global Trash Hero dengan membagikan posting inspirasional dari chapter lain
– mendorong langkah kecil dengan menunjukan dampak yang lebih luas: isu atau aksi lokal pasti ada hubungannya dengan masalah global, begitu pula sebaliknya. Hal ini akan menyampaikan pesan bahwa setiap aksi maupun setiap orang dapat memberikan dampak positif… bersama kita bisa membuat perubahan!
MENGINFORMASIKAN
– memastikan masyarakat mengetahui perkembangan terbaru tentang program Trash Hero dan pencapaian chapter Anda
– menunjukkan transparansi. Hal ini sangat penting di Trash Hero
– Mendokumentasikan foto dan statistik kegiatan chapter Anda untuk dimasukkan dalam database Trash Hero World
MENUNJUKKAN APRESIASI
– memastikan sponsor dan relawan diumumkan dan diberi ucapan terima kasih secara publik
– memberi publikasi gratis di media sosial pada bisnis yang mengambil langkah peduli lingkungan
Media sosial juga merupakan sarana yang baik untuk komunikasi internal, yang akan membantu Anda membangun jejaring lokal:
– gunakan Messenger / Line / WhatsApp untuk menciptakan grup chat dengan misalnya para sponsor, mitra program botol dan tas, pengurus chapter, dan relawan umum. Dengan cara ini, Anda menciptakan rasa memiliki, dan ini juga akan memudahkan Anda untuk menyebarkan informasi, mendapat umpan balik, dan mendapat dukungan dengan cepat
– jika memungkinkan, tag relawan yang hadir pada aksi bersih pada foto grup. Hal ini akan membuat foto tidak hanya dilihat oleh orang yang menyukai laman Facebook chapter Anda, tetapi juga oleh teman-teman dari relawan Anda
Apa dan bagaimana cara membuat posting?
Bagi Trash Hero, hal yang terpenting adalah untuk memposting hal yang positif dan optimis. Buatlah posting yang relevan, dengan referensi lokal jika memungkinkan, dan pastikan tidak ada muatan politik di dalamnya. Postinglah foto dan video, dan cobalah untuk menambahkan teks baik dalam Bahasa Indonesia maupun Bahasa Inggris. Kualitas posting tidak perlu sempurna, yang penting cerita Anda tersampaikan dengan baik. Berikut adalah hal-hal yang dapat menjadi bahan posting:
- Setiap kegiatan aksi bersih harus dibuat di satu album dan post (lihat: Aksi bersih)
- Iklankan kegiatan lain atau aksi lain yang Anda lakukan, pastikan Anda hanya memuat foto orang yang bahagia dan tersenyum. Ucapan terima kasih kepada sponsor yang telah memberikan dukungan berapapun
besarnya.
- “Meet a Trash Hero”- sebuah wawancara singkat dan foto mengenai salah satu relawan aksi bersih yang menjelaskan mengapa mereka bergabung dengan Trash Hero.
- Informasi mengenai program botol dan tas, juga jika chapter Anda mendapat mitra baru.
- Dukungan untuk program atau grup lain di lingkungan Anda yang memiliki kegiatan sejenis aksi bersih Trash Hero, misalnya dengan membagikan pengumuman tentang rencana aksi bersih mereka.
- Membagikan posting Trash Hero dari chapter lain dan negara lain.
- Membagikan artikel atau video mengenai sampah dan polusi plastik, dengan tulisan yang menjelaskan bahwa topik tersebut relevan dengan kondisi lokal. Hindari gambar atau pesan yang negatif.
Jika karena alasan tertentu Anda tidak memiliki berita untuk dipost, Anda bisa membagikan misalnya keindahan matahari terbenam di tempat Anda? Dengan merayakan keindahan alam di tempat Anda, Anda mengingatkan orang lain untuk terus menjaganya tetap bersih.
Usahakan untuk setidaknya membuat posting 2 atau 3 kali per minggu atau lebih, asalkan tidak lebih dari satu posting per harinya.
Facebook memiliki alat untuk membuat Anda terorganisir, sebagai contoh Anda bisa membuat posting yang dijadwalkan untuk dipost secara otomatis pada waktu yang sudah ditentukan sebelumnya; gunakan fasilitas “event” untuk mempromosikan rencana aksi bersih; dan gunakan album foto untuk memisahkan cerita- cerita tentang aksi bersih, sponsor, jaringan air minum isi ulang, dan lain sebagainya.
Aturan dasar komunikasi
Ketika laman Facebook chapter Anda mulai mendapatkan dukungan dari masyarakat lokal,
Anda akan mendapat komentar dan pesan pada postingan Anda. Belum tentu semuanya akan bernada positif. Ingatlah beberapa hal ketika Anda menjawab komentar mereka:
– Trash Hero tidak menghakimi orang lain. Artinya kita tidak menyalahkan atau membuat orang merasa bersalah.
– Jangan berargumen. Hal ini tidak produktif. Berilah tanggapan dengan cara yang baik dan ramah, serta fokuslah pada misi dan pencapaian Trash Hero.
– Pastikan semua komunikasi dilakukan secara sopan dan optimis.
Di luar laman Facebook: menggunakan media lain
Facebook adalah fokus utama kami. Namun, kami juga aktif di Instagram, dan chapter Anda dapat menggunakan platform ini, Twitter, atau saluran media sosial lokal lainnya. Harap beri tahu tim mentor di negara Anda jika Anda ingin membuka akun media sosial baru, dan ikuti lah pedoman yang dijelasskan di atas untuk setiap akun.
Trash Hero World memiliki channel YouTube, dan kami juga memiliki beberapa channel Trash Hero berbasis negara. Kami menyarankan para chapter untuk membagikan video mereka melalui channel YouTube Trash Hero negara dibanding membuat channel sendiri. Jika Anda memiliki klip yang bagus untuk dibagikan, informasikan kepada tim mentor Anda dan mereka akan mengunggahnya ke salah satu saluran YouTube kami, dan memberi kredit pada chapter Anda.
Pendekatan pada media tradisional: TV, surat kabar, dsb
Liputan media akan sangat baik karena hal itu membantu penyebaran pesan mengenai Trash Hero. Tetapi hal ini dapat berisiko karena kita tidak bisa mengendalikan bagaimana aktivitas kita ditayangkan.
Sangat disarankan bagi Anda untuk mengontak media lokal (TV, surat kabar, dsb) sesaat setelah Anda memulai chapter Anda. Bangunlah hubungan baik dengan mereka, informasikan kepada mereka mengenai acara-acara khusus pada chapter Anda, dan undang mereka untuk bergabung pada acara-acara tersebut. Setelah Anda memiliki jaringan, media nasional dan internasional mungkin akan menghubungi Anda secara langsung.
 Jika Anda dihubungi oleh media luar (TV, blogger, atau majalah) untuk diwawancara, pastikan bahwa sejak awal mereka memahami tentang apa itu Trash Hero dan tentang nilai-nilai positif inklusivitas yang kita gunakan. Disarankan juga untuk memeriksa tema yang akan mereka angkat sebelum Anda menyetujuinya.
Jika Anda dihubungi oleh media luar (TV, blogger, atau majalah) untuk diwawancara, pastikan bahwa sejak awal mereka memahami tentang apa itu Trash Hero dan tentang nilai-nilai positif inklusivitas yang kita gunakan. Disarankan juga untuk memeriksa tema yang akan mereka angkat sebelum Anda menyetujuinya.
Sebagai contoh, sebelumnya terdapat kasus di mana sebuah portal berita yang hendak meliput sepasang orang asing yang melakukan aksi bersih dengan tujuan agar orang lokal merasa malu, ketimbang meliput aksi bersih tersebut sebagai kegiatan komunitas secara keseluruhan.
Dalam setiap wawancara, gunakanlah kaos Trash Hero, bahkan dalam wawancara di radio. Hal ini akan memberikan Anda rasa percaya diri dan akan menghasilkan foto-foto yang bagus untuk dipublikasikan kemudian. Apapun pertanyaan yang dilontarkan pada Anda, tetaplah bersikap positif dan selalu yakin tentang apa yang Anda katakan (jangan membuat kalimat yang tidak bisa Anda pertanggungjawabkan hanya karena Anda merasa tertekan!)
Selalu alihkan pembahasan tentang siapa yang perlu disalahkan terkait permasalah sampah, menjadi pembahasan yang positif, misalnya: “kami rasa, menentukan siapa yang salah tidak akan memperbaiki keadaan, kami lebih berfokus pada upaya menyatukan semua pihak dan mencari solusi.” Anda tidak perlu memaksa diri Anda untuk menjawab semua pertanyaan: mengatakan “saya tidak tahu” tidaklah masalah.
 Jika Anda merasa grogi, cobalah untuk tetap tenang. Anda tidak harus menjadi juru bicara ahli, jawablah dari hati Anda, dan berpeganglah pada nilai-nilai yang Anda anggap benar. Anda dapat mempersiapkan diri dengan menonton beberapa video dan membaca artikel-artikel dari chapter Trash Hero lain untuk melihat bagaimana mereka melakukannya.
Jika Anda merasa grogi, cobalah untuk tetap tenang. Anda tidak harus menjadi juru bicara ahli, jawablah dari hati Anda, dan berpeganglah pada nilai-nilai yang Anda anggap benar. Anda dapat mempersiapkan diri dengan menonton beberapa video dan membaca artikel-artikel dari chapter Trash Hero lain untuk melihat bagaimana mereka melakukannya.
Jika Anda mendapat pertanyaan secara tertulis, Anda akan lebih mudah menjawabnya karena Anda bisa mendapat informasi umum di website Trash Hero dan di dokumen ini yang dapat Anda gunakan sebagai acuan.
Setelah wawancara selesai, mintalah versi final sebelum hal tersebut ditayangkan. Hal ini tidak selalu memungkinkan, tetapi sangatlah penting untuk diupayakan: publikasi yang buruk tidak hanya akan merusak reputasi chapter Anda tetapi juga merusak reputasi Trash Hero secara global. Jika Anda melihat bagian di mana Anda merasa kurang yakin atau nyaman dengan hasil tersebut, kontaklah tim mentor Anda untuk memeriksanya.
Bagi semua liputan media di seluruh kanal sosial media Anda, dengan tautan jika memungkinkan.
“Apapun media yang Anda gunakan, pastikan Anda selalu berkomunikasi dengan sopan dan positif.”
⬆ Kembali ke atas ⬆
9. Mendapatkan sponsor
Dukungan lokal adalah kunci kesuksesan chapter Anda. Sponsor harus berasal dari komunitas Anda dan semua orang atau pihak memiliki kesempatan yang sama untuk berpartisipasi. Usaha kecil sama pentingnya dengan usaha besar.
Jika seseorang di tim Anda memiliki sebuah usaha, akan sangat praktis jika mereka menjadi sponsor semua aktivitas di masa-masa awal berdirinya chapter. Tetapi tolong jangan lakukan itu! Adalah penting bahwa tidak ada satupun bisnis yang berkaitan secara langsung dengan Trash Hero. Sebagai contoh, usaha tersebut boleh mensponsori aksi bersih, tetapi tidak boleh menjadi sponsor tunggal, dan lokasi bisnis mereka tidak boleh menjadi lokasi titik bertemu aksi bersih. Orang lain mungkin akan enggan terlibat dengan Trash Hero jika mereka berpikir kegiatan ini adalah ajang untuk mempromosikan sebuah usaha atau Anda terlihat seperti mendapat keuntungan pribadi.
 Bagaimana cara mendekati pelaku usaha
Bagaimana cara mendekati pelaku usaha
Gunakan jaringan Anda untuk mendapat kontak para pelaku bisnis. Jika Anda mendapat kontak yang direkomendasikan oleh seseorang, maka akan lebih mudah bagi Anda untuk menghubungi mereka. Tergantung dari besarnya dan lokasi bisnis, Anda dapat mulai menghubungi mereka melalui email, telepon, atau pertemuan langsung.
Jika Anda berniat untuk bertemu secara langsung dan Anda tidak tahu harus bertemu siapa, mintalah untuk bertemu dengan manajer atau pemilik usaha. Jika mereka tidak tersedia, aturlah pertemuan di kemudian hari (hal ini lebih mudah dilakukan jika Anda menghubungi via telepon atau email). Gunakanlah kaos Trash Hero sehingga Anda netral dan tidak mewakili suatu usaha di area tersebut.
Persiapkan diri Anda dengan baik: dapatkah Anda menjelaskan misi Trash Hero dan melakukan pendekatan dalam 2 hingga 10 menit? Anda tidak pernah tahu berapa lama waktu yang Anda dapatkah. Jelaskan secara spesifik bagaimana bisnis mereka dapat berkontribusi dan bantuan jenis apa yang Anda butuhkan.
 Jangan meminta terlalu banyak dukungan di awal kerjasama. Bisnis dapat mendonasikan sedikit terlebih dahulu, dan jika mereka senang dengan bentuk kerjasama dengan Anda, mereka akan memberi bantuan lebih. Sebagai contoh: mintalah 50 karung sampah atau 2 buah nanas untuk konsumsi di aksi bersih selanjutnya.
Jangan meminta terlalu banyak dukungan di awal kerjasama. Bisnis dapat mendonasikan sedikit terlebih dahulu, dan jika mereka senang dengan bentuk kerjasama dengan Anda, mereka akan memberi bantuan lebih. Sebagai contoh: mintalah 50 karung sampah atau 2 buah nanas untuk konsumsi di aksi bersih selanjutnya.
Setelah Anda mendapat kepercayaan dari mereka, cobalah untuk membuat persetujuan dengan sebuah bisnis untuk menyediakan dukungan secara reguler. Sebagai contoh: Resort A menyediakan makanan gratis untuk para relawan setelah aksi bersih sebanyak satu kali per bulan. Hal ini juga dapat membantu Anda dalam menyusun perencanaan.
Pastikan untuk tidak menerima donasi dalam bentuk uang secara umum, dan bahwa mereka tahu bahwa Anda adalah relawan. Jika Anda memiliki waktu, tunjukkan kepada mereka beberapa foto Trash Hero menggunakan smartphone atau laptop atau buatlah presentasi singkat mengenai Trash Hero.
Selalu berikan mereka nomor kontak dan alamat website maupun Facebook agar mereka dapat mencari info tentang chapter Anda lebih jauh jika mereka tertarik.
Tanyakan pada tim mentor atau chapter lokal lain di negara Anda, apakah mereka memiliki format email yang dapat Anda gunakan dan modifikasi, misalnya:
– surat untuk memperkenalkan program botol undangan aksi bersih untuk para staf di sebuah
usaha
– Anda bisa menghubungi chapter-chapter lain melalui intranet.
Menjaga hubungan dengan para sponsor
Pastikan semua sponsor mendapat informasi mengenai kegiatan Anda dan pastikan pula bahwa semua pihak yang terlibat mengetahui bahwa kegiatan aksi bersih Anda terlaksana karena dukungan para sponsor. Sebagai contoh, taruhlah ucapan terima kasih kepada sponsor di grup Line/WA atau kirimlah para sponsor email secara berkala yang berisi tentang update, daftar kebutuhan, serta kuitansi untuk menunjukkan bahwa Anda bersifat transparan. Anda dapat juga melibatkan pemerintah atau organisasi lainnya dalam grup chat ini.
Tetaplah positif
Beberapa pihak memerlukan waktu lebih lama untuk memahami apa itu Trash Hero. Jadi, sangatlah wajar jika beberapa bisnis tidak langsung berminat untuk terlibat. Tetapi akan selalu ada pihak yang akan mendukung Anda, dan setelah Anda memposting kegiatan Anda di sosial media, Anda akan melihat bahwa orang- orang akan turut mendukung Anda.
Sayangnya, Anda juga mungkin akan menemukan pihak yang bersikap negatif terhadap Anda secara pribadi maupun kepada Trash Hero secara umum. Ingatlah untuk tetap gembira dan positif, dan yakinlah bahwa akan selalu ada harapan 🙂
Catatan: Jika Anda memiliki sponsor yang mungkin berminat untuk mendukung gerakan global melalui donasi, mohon informasikan hal tersebut kepada tim di negara Anda atau Trash Hero World. Donasi dalam bentuk uang tidak diperbolehkan untuk diterima oleh chapter lokal.
⬆ Kembali ke atas ⬆
10. Mengelola relawan
Membangun partisipasi
Bahkan setelah chapter Anda terbentuk, Anda tetap perlu untuk membangun partisipasi masyarakat di kegiatan Trash Hero.
– Pastikan anggota tim inti dan kegiatan chapter Anda selalu terbuka bagi pendatang baru
– Iklankan kebutuhan relawan di sosial media — baik melalui jaringan yang Anda miliki maupun melalui grup-grup lokal
– Ajaklah orang untuk membawa teman ke acara aksi bersih
– Distribusikan poster ke tempat-tempat baru, tanyakan media lokal apakah mereka mengijinkan Anda memasang iklan kegiatan secara gratis, atau dekati pengelola bisnis untuk memasang video Trash Hero di toko mereka.
Silakan berkreasi!
Menyediakan pelatihan
Setelah Anda mendapat lebih banyak pengalaman, bagikanlah pengetahuan yang Anda dapat kepada anggota tim. Berilah kesempatan kepada relawan reguler untuk melakukan tanggung jawab yang lebih besar agar mereka terpacu untuk tetap tergabung dengan Trash Hero, dan juga agar beban Anda menjadi lebih ringan. Sebagai contoh mereka dapat mendistribusikan poster aksi bersih atau menjadi petugas foto di acara aksi bersih.
Merayakan keberhasilan setiap saat
Seiring berjalannya waktu, Anda mungkin tidak lagi terlalu ingin merayakan pencapaian yang telah Anda buat. Tetapi hal ini sangat penting untuk dilakukan agar bisa memotivasi para relawan. Periksa apakah Anda akan memiliki momentum untuk dirayakan — misalnya aksi bersih ke-50, atau saat chapter Anda berulang tahun. Anda bisa merencanakan aksi bersih di lokasi spesial, atau mendapat sponsor spesial yang menyediakan kue ulang tahun atau hadiah untuk relawan.
Mengelola konflik
Terkadang Anda mungkin akan menemukan orang-orang yang mengkritik tim Anda atau mengkritik Trash Hero secara umum. Biasanya hal ini disebabkan karena mereka tidak setuju dengan pendekatan yang kita lakukan, atau mereka berpikir mereka bisa mencapai hasil yang lebih baik dengan melakukan cara lain. Dalam kasus ini atau kasus apapun, sangatlah penting bagi kita untuk tidak terpancing emosi, melontarkan sindiran, atau terlalu memasukkan ke dalam hati, karena hal-hal itu akan memperbesar masalah.
Jika komentar dibuat di ranah publik dunia maya, usahakan untuk membawa diskusi ke jalur pribadi atau bertemu muka. Komunikasi tatap muka atau telepon biasanya akan membantu meredam situasi dan menghindarkan kesalahpahaman. Secara umum, disarankan untuk tidak menghapus komentar kecuali jika komentar tersebut menyerang pribadi seseorang atau mengandung ujaran kebencian.
Dalam diskusi apapun, jadilah pendengar yang baik dan cobalah untuk memahami inti masalah yang dibicarakan, dan jelaskanlah kebijakan kita yang berhubungan dengan masalah tersebut — selalu gunakan dokumen ini sebagai “pedoman resmi”. Hargailah semua sudut pandang dan emosi yang diungkapkan oleh setiap orang.
Jika Anda memerlukan bantuan untuk mengatasi konflik atau membuat komentar balasan, silakan hubungi tim mentor atau tanyalah saran melalui Trash Hero Family intranet.
⬆ Back to contents ⬆
11. Pantang menyerah!
 Jalan menuju perubahan yang lebih baik dapat dipenuhi oleh rasa frustasi, kekecewaan, kebosanan, dan bahkan ketakutan. Ingatlah bahwa Anda memiliki keluarga besar Trash Hero di belakang Anda, dan bahwa membersihkan hal-hal negatif adalah keahlian kita 😉 Percayalah pada misi dan diri Anda, dan terimalah fakta bahwa memulai dan membawa perubahan membutuhkan waktu yang tidak sebentar.
Jalan menuju perubahan yang lebih baik dapat dipenuhi oleh rasa frustasi, kekecewaan, kebosanan, dan bahkan ketakutan. Ingatlah bahwa Anda memiliki keluarga besar Trash Hero di belakang Anda, dan bahwa membersihkan hal-hal negatif adalah keahlian kita 😉 Percayalah pada misi dan diri Anda, dan terimalah fakta bahwa memulai dan membawa perubahan membutuhkan waktu yang tidak sebentar.
Menghadapi kritik dan opini negatif
Trash Hero sangat mudah terlihat di muka umum, dan setiap orang memiliki pendapat pribadi mengenai Trash Hero. Mayoritas dari mereka akan berpendapat positif dan mendukung kegiatan yang kita lakukan; namun akan ada sebagian kecil yang mengkritik, merendahkan, atau bahkan menyerang. Akan sangat membantu jika Anda tidak terfokus pada hal negatif atau memasukkannya ke dalam hati. Tetaplah netral dan bersahabat. Mungkin saja orang tersebut belum terlalu memahami pendekatan yang dilakukan Trash Hero, atau tidak mengetahui bahwa kita semua adalah relawan.
Di sisi lain, terimalah masukan yang mereka berikan dengan serius dan cobalah untuk memahami posisi dari sudut pandang berbeda, atau alasan mengapa mereka berpendapat negatif. Jika Anda mengalami konflik saat bertatap muka, tunjukkanlah bahwa Anda benar- benar mendengarkan mereka. Kalimat “Saya mengeri maksud Anda tetapi kami memilih untuk menggunakan pendekatan lain” biasanya dapat menetralkan situasi.
Jika Anda memiliki seorang anggota tim yang selalu berpandangan negatif, Anda perlu berbicara secara terbuka terhadap mereka dan berusaha mencari solusi bersama. Mungkin mereka merasa kontribusi mereka kurang dihargai atau mungkin mereka lebih cocok untuk bergerak di organisasi lain yang menggunakan pendekatan berbeda.
Jika Anda membutuhkan saran mengenai situasi tertentu, konsultasikanlah hal tersebut dengan tim Anda, tim mentor, atau chapter Trash Hero.
Mengatasi minimnya sponsor atau relawan
Mungkin saja Anda sedang mengalami masa sepi atau kehilangan momentum, di mana Anda menyadari bahwa sponsor tidak seantusias sebelumnya dan jumlah relawan yang datang semakin sedikit. Bisa juga Anda baru mulai merintis dan frustasi karena minimnya dukungan dari masyarakat.
Masyarakat memerlukan waktu untuk memahami misi yang Trash Hero bawa dan untuk membangun kepercayaan pada Trash Hero. Juga dibutuhkan usaha yang cukup besar untuk tetap membuat kegiatan chapter Anda berjalan setiap minggunya. Terbukalah dengan tim Anda mengenai hal ini dan kreatiflah dalam mencari solusi. Anda mungkin akan menemukan ide baru setelah berbincang dengan anggota tim atau dengan teman-teman Trash Hero dari chapter lain.
Selalu ingat bahwa kesuksesan tidak diukur lewat angka. Cobalah untuk menilai dan merayakan keberhasilan dalam bentuk lain yang tim Anda capai. Hal ini dapat memberi semangat baru bagi Anda dan anggota tim.

Sebagai contoh, terdapat cerita dari sebuah chapter di mana setelah bekerjasama selama beberapa minggu dengan pengelola Taman Nasional, chapter tersebut mendapati adanya perubahan pada papan pengumuman yang dipasang di wilayah tersebut. Isi pesan dari papan tersebut berubah dari “Denda US$ 15 bagi orang yang membuang sampah” menjadi pesan yang lebih lembut: “Mari bersama-sama menjaga kebersihan Taman Nasional – jadilah pahlawan!”.

Lihatlah perubahan-perubahan kecil seperti ini di sekitar Anda: meski Anda tidak dapat mengklaim bahwa ini hasil kerja Anda, ini adalah hal yang menakjubkan untuk dilihat dan sama berharganya dengan prestasi jumlah relawan.
Mengatasi tekanan dan rasa lelah pada tim Anda
Masalah: Terdapat banyak tugas yang harus diselesaikan dalam waktu singkat dengan jumlah orang yang sedikit.
Solusi: Duduk bersama dan tinjau kembali apakah tugas-tugas tersebut dapat digabungkan? Apakah tugas-tugas tersebut penting untuk dilakukan? Buatlah prioritas dan fokuslah pada satu atau dua hal yang paling penting terlebih dahulu.
Masalah: Suatu tugas terasa membebani dan membosankan seiring waktu.
Solusi: Lihatlah kemungkinan untuk bertukar tugas dengan anggota tim lain, atau ajaklah orang lain untuk melakukan tugas tersebut melalui Facebook atau dengan mengumumkannya saat aksi bersih.
Masalah: Anda merasa sangat antusias dan ingin melakukan banyak projek atau terlibat di kegiatan lokal lainnya dalam waktu yang bersamaan.
Solusi: Fokus dan rem! Tentu Anda ingin melakukan banyak hal dengan cepat dan dengan hasil terbaik. Tetapi cobalah untuk berkonsentrasi pada tugas pertama secara benar, niscaya kesuksesan penyelesaian tugas lain akan menyusul.
Masalah: Anda merasa Anda melakukan tugas tanpa henti untuk Trash Hero, sedangkan pekerjaan Anda agak terlalaikan, atau Anda merasa jenuh.
Solusi: Sederhana, beristirahatlah! Liburkan kegiatan aksi bersih untuk satu atau dua minggu, berliburlah selama beberapa waktu, atau batasi waktu Anda untuk melakukan tugas Trash Hero pada waktu tersebut. Ini bukanlah kegagalan tetapi merupakan hal yang perlu dilakukan — dan Anda akan kembali aktif dengan lebih banyak energi, ide, dan antusiasme.
Ingat, bukan hanya Anda yang mengalami hal semacam ini. Tetaplah berpegang pada pendekatan Trash Hero, bersabarlah dengan diri Anda dan dengan orang-orang di sekitar Anda, serta mintalah umpan balik atau saran dari orang lain. Keunikan yang dimiliki Trash Hero adalah kita selalu terbuka satu sama lain.
⬆ Kembali ke atas ⬆
12. Mendukung misi Trash Hero yang lebih luas
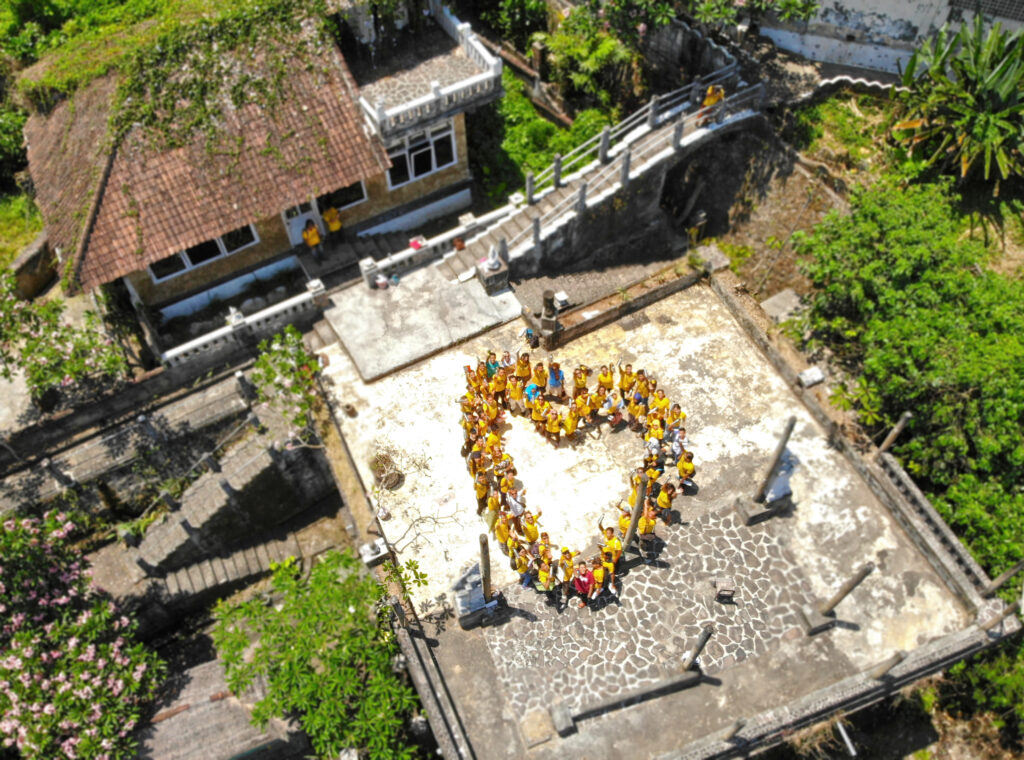
Sebagai seorang Trash Hero, Anda adalah bagian dari jejaring keluarga kami dan Anda menolong kami untuk menyebarkan pesan ke seluruh dunia. Menjadi seorang panutan adalah penting: aksi Anda mencerminkan misi kami semua, dan sikap Anda dapat menginspirasi orang lain untuk bergabung. Chapter baru Trash Hero biasanya dibentuk setelah beberapa orang bergabung dalam suatu aksi bersih di chapter lain dan terinspirasi untuk melakukan hal yang sama
Beberapa hal yang dapat Anda lakukan untuk mengembangkan dan memperkuat jaringan:
- Berbagi cerita dengan organisasi lain di negara Anda atau organisasi dunia. Anda dapat melakukan ini dengan men-tag mereka di post Facebook, mengirim email, atau berbagi cerita melalui Trash Hero Family intranet.
- Berpartisipasi dalam diskusi di intranet, bagikan pengalaman Anda, dan bersedialah untuk membantu.
- Selalu menjadi contoh yang baik saat kita membawa nama Trash Hero. Sebagai contoh, tolaklah plastik setiap saat dan jangan gunakan sedotan, kantung atau botol plastik di kehidupan sehari-hari.
- Di negara di mana terdapat banyak chapter Trash Hero yang aktif, kami menyelenggarakan pertemuan keluarga Trash Hero untuk berbagi pengalaman dan belajar dari satu sama lain. Berusahalah untuk mengikuti acara ini — ini adalah cara baik untuk mengenal teman-teman Trash Hero dari chapter lain dan mendapat motivasi untuk mesukseskan program-program di masa yang akan datang.
- Ketika Anda lebih berpengalaman Anda dapat bergabung di tim mentor dan membantu untuk membangun dan mendukung chapter Trash Hero lain.
- Ikuti pedoman branding saat membuat materi untuk chapter Anda. Branding Trash Hero harus selalu konsisten dan terlihat profesional. Tim desain kami dapat menolong Anda dalam hal ini.
- Jika Anda memiliki kontak atau teman yang ingin membantu tetapi tinggal di lokasi lain, arahkan mereka pada website Trash Hero. Kami selalu membuka kesempatan untuk relawan yang memiliki keahlian khusus.
Bersama kita akan membuat perubahan! Jika Anda masih membaca hingga sejauh ini, Anda adalah pahlawan sesuangguhnya. 😉
⬆ Kembali ke atas ⬆
Ada hal lain yang ingin Anda tambahkan?
Kami telah membuat dokumen ini semudah mungkin untuk dimengerti. Tetapi jika Anda menemukan sesuatu yang kurang lengkap atau ingin mengajukan saran untuk edisi selanjutnya, silakan hubungi kami.
Untuk pertanyaan terkait pengelolaan chapter Anda, kontaklah selalu tim mentor Anda terlebih dahulu. Terima kasih!
read more












 Aksi Bersih
Aksi Bersih Program Botol dan Tas Pakai Ulang
Program Botol dan Tas Pakai Ulang Pendidikan dan Anak-anak
Pendidikan dan Anak-anak Tim yang baik adalah syarat penting dari kesuksesan sebuah chapter. Paling tidak sebuah tim memiliki 3 orang anggota, termasuk paling tidak satu orang yang terhubung secara baik dengan komunitas lokal. Jumlah optimal anggota sebuah tim adalah 5-6 orang.
Tim yang baik adalah syarat penting dari kesuksesan sebuah chapter. Paling tidak sebuah tim memiliki 3 orang anggota, termasuk paling tidak satu orang yang terhubung secara baik dengan komunitas lokal. Jumlah optimal anggota sebuah tim adalah 5-6 orang.
 Kita memiliki pedoman atas penggunaan logo, warna, dan font di sini, beserta beberapa template untuk digunakan sebagai bahan marketing penting. Anda dapat memperoleh akses untuk mengunduh template ini setelah chapter Anda terbentuk.
Kita memiliki pedoman atas penggunaan logo, warna, dan font di sini, beserta beberapa template untuk digunakan sebagai bahan marketing penting. Anda dapat memperoleh akses untuk mengunduh template ini setelah chapter Anda terbentuk.

 Menginformasikan kegiatan aksi bersih kepada orang-orang
Menginformasikan kegiatan aksi bersih kepada orang-orang Ada beberapa kemungkinan cara kerjasama: pelaku usaha daerah atau dinas kota dapat membantu menyediakan beberapa alat kebersihan, dinas kebersihan setempat dapat membantu dalam penjemputan sampah, restoran atau hotel dapat memberikan air atau makanan bagi relawan, pengusaha laundri lokal dapat mencuci sarung tangan, dan pihak-pihak lain yang mungkin membantu. (Lihat:
Ada beberapa kemungkinan cara kerjasama: pelaku usaha daerah atau dinas kota dapat membantu menyediakan beberapa alat kebersihan, dinas kebersihan setempat dapat membantu dalam penjemputan sampah, restoran atau hotel dapat memberikan air atau makanan bagi relawan, pengusaha laundri lokal dapat mencuci sarung tangan, dan pihak-pihak lain yang mungkin membantu. (Lihat:  Berikan penjelasan: Sambutlah semua orang yang hadir dan ucapkan terima kasih atas kehadiran mereka. Perkenalkan Trash Hero secara singkat dan jelaskan misi serta latar belakang singkat Trash Hero. Jelaskan rencana yang akan dilakukan pada hari tersebut (lihat poin sebelumnya). Ingatkan semua orang untuk bersenang-senang, beristirahat (jika perlu), minum air, dan percaya bahwa upaya mereka mengambil berapapun jumlah sampah akan sangat berharga.
Berikan penjelasan: Sambutlah semua orang yang hadir dan ucapkan terima kasih atas kehadiran mereka. Perkenalkan Trash Hero secara singkat dan jelaskan misi serta latar belakang singkat Trash Hero. Jelaskan rencana yang akan dilakukan pada hari tersebut (lihat poin sebelumnya). Ingatkan semua orang untuk bersenang-senang, beristirahat (jika perlu), minum air, dan percaya bahwa upaya mereka mengambil berapapun jumlah sampah akan sangat berharga. 1. Tanggal aksi bersih
1. Tanggal aksi bersih
 Ini adalah pertanyaan yang hampir selalu ditanyakan oleh orang pada saat aksi berih. Jawabannya bergantung pada lokasi dan sistem pengelolaan sampah di lokasi tersebut.
Ini adalah pertanyaan yang hampir selalu ditanyakan oleh orang pada saat aksi berih. Jawabannya bergantung pada lokasi dan sistem pengelolaan sampah di lokasi tersebut. APAKAH ANDA TAHU? Meski plastik PET dapat didaur ulang, jumlah botol PET di dunia yang mengandung bahan daur ulang hanya berkisar kurang dari 7%. Hal ini karena biasanya botol PET yang didaur ulang digunakan untuk membuat kain sintetis yang akan menjadi pakaian, karpet dan kemasan. Kain ini
APAKAH ANDA TAHU? Meski plastik PET dapat didaur ulang, jumlah botol PET di dunia yang mengandung bahan daur ulang hanya berkisar kurang dari 7%. Hal ini karena biasanya botol PET yang didaur ulang digunakan untuk membuat kain sintetis yang akan menjadi pakaian, karpet dan kemasan. Kain ini 

 Jika kita teliti lebih lanjut label-label tersebut, seringkali bahan-bahan ini hanya bisa dikompos di fasilitas industri, di mana sampah bioplastik akan dipanaskan sampai 60C. Pada fasilitas ini bioplastik biasanya dipecah menjadi karbon dioksida dan air, sehingga tidak ada nutrisi tersisa yang bisa dijadikan kompos. Tidak ada studi yang menunjukkan apa yang akan terjadi pada zat kimia lain yang terdapat pada bioplastik tersebut. Zat-zat ini adalah zat-zat yang sama dengan plastik konvensional. Asam polilaktat atau PLA, jenis bioplastik yang umum diproduksi, telah diketahui mengandung jumlah racun yang sama-sama berbahayanya dengan PVC.
Jika kita teliti lebih lanjut label-label tersebut, seringkali bahan-bahan ini hanya bisa dikompos di fasilitas industri, di mana sampah bioplastik akan dipanaskan sampai 60C. Pada fasilitas ini bioplastik biasanya dipecah menjadi karbon dioksida dan air, sehingga tidak ada nutrisi tersisa yang bisa dijadikan kompos. Tidak ada studi yang menunjukkan apa yang akan terjadi pada zat kimia lain yang terdapat pada bioplastik tersebut. Zat-zat ini adalah zat-zat yang sama dengan plastik konvensional. Asam polilaktat atau PLA, jenis bioplastik yang umum diproduksi, telah diketahui mengandung jumlah racun yang sama-sama berbahayanya dengan PVC.

 Program ini menyediakan botol minum stainless steel yang dijual kepada pelaku usaha lokal, untuk dijual kembali kepada pelanggan mereka dengan sedikit keuntungan. Jumlah keuntungan ini akan digunakan untuk menyediakan air minum isi ulang gratis kepada pelanggan yang memiliki botol minum Trash Hero, di manapun mereka membeli botol tersebut.
Program ini menyediakan botol minum stainless steel yang dijual kepada pelaku usaha lokal, untuk dijual kembali kepada pelanggan mereka dengan sedikit keuntungan. Jumlah keuntungan ini akan digunakan untuk menyediakan air minum isi ulang gratis kepada pelanggan yang memiliki botol minum Trash Hero, di manapun mereka membeli botol tersebut. Saat ini barang diimpor dari Cina, dan kami masih mencari produsen lokal. Trash Hero memiliki sertifikat mengenai kualitas dan komposisi bahan menyusun botol tersebut untuk ditunjukkan kepada pada pelaku usaha dan pelanggan mereka.
Saat ini barang diimpor dari Cina, dan kami masih mencari produsen lokal. Trash Hero memiliki sertifikat mengenai kualitas dan komposisi bahan menyusun botol tersebut untuk ditunjukkan kepada pada pelaku usaha dan pelanggan mereka.
 Media sosial
Media sosial Mengenai tas pakai ulang Trash Hero
Mengenai tas pakai ulang Trash Hero Cara melakukan pemesanan
Cara melakukan pemesanan Anak anak, remaja, dan keluarga mereka adalah bagian penting dalam gerakan ini. Kita memiliki materi pendidikan untuk umum serta program yang didesain khusus untuk anak-anak di mana chapter dapat menjalankannya dengan melibatkan anak-anak di lingkungan sekitar.
Anak anak, remaja, dan keluarga mereka adalah bagian penting dalam gerakan ini. Kita memiliki materi pendidikan untuk umum serta program yang didesain khusus untuk anak-anak di mana chapter dapat menjalankannya dengan melibatkan anak-anak di lingkungan sekitar.
 Seringkali terdapat acara yang diselenggarakan oleh perkumpulan hotel atau pebisnis di mana Anda dapat mempresentasikan dan menjelaskan tentang bagaimana perusahaan dapat ambil bagian dalam melakukan aksi. Tanyakan apakah mereka akan memperkenalkan Trash Hero kepada para anggota mereka dan mengirim karyawan mereka pada acara aksi bersih mingguan, atau mungkin memberi bantuan jasa pada chapter Anda.
Seringkali terdapat acara yang diselenggarakan oleh perkumpulan hotel atau pebisnis di mana Anda dapat mempresentasikan dan menjelaskan tentang bagaimana perusahaan dapat ambil bagian dalam melakukan aksi. Tanyakan apakah mereka akan memperkenalkan Trash Hero kepada para anggota mereka dan mengirim karyawan mereka pada acara aksi bersih mingguan, atau mungkin memberi bantuan jasa pada chapter Anda. Berkolaborasilah dengan organisasi swadaya lainnya atau di kegiatan peduli lingkungan di lingkunganmu atau kegiatan global. Kita tidak berkompetisi dengan siapapun: hanya dengan bekerja bersamalah kita dapat membuat perubahan.
Berkolaborasilah dengan organisasi swadaya lainnya atau di kegiatan peduli lingkungan di lingkunganmu atau kegiatan global. Kita tidak berkompetisi dengan siapapun: hanya dengan bekerja bersamalah kita dapat membuat perubahan. Jika Anda memiliki hubungan baik dengan pemerintah lokal, Anda dapat memperbaiki kondisi lingkungan di wilayah Anda dengan memperkenalkan masyarakat dengan orang yang tepat untuk berdiskusi dan menerapkan solusi, misalnya dengan menyediakan lebih banyak tempat sampah untuk masyarakat umum. Pelaku usaha dapat memberi sponsor dengan cara menyediakan barang dan membayar pegawai untuk mengangkut sampah, dengan timbal balik berupa penulisan logo usaha di tempat sampah tersebut.
Jika Anda memiliki hubungan baik dengan pemerintah lokal, Anda dapat memperbaiki kondisi lingkungan di wilayah Anda dengan memperkenalkan masyarakat dengan orang yang tepat untuk berdiskusi dan menerapkan solusi, misalnya dengan menyediakan lebih banyak tempat sampah untuk masyarakat umum. Pelaku usaha dapat memberi sponsor dengan cara menyediakan barang dan membayar pegawai untuk mengangkut sampah, dengan timbal balik berupa penulisan logo usaha di tempat sampah tersebut.
 Jika Anda dihubungi oleh media luar (TV, blogger, atau majalah) untuk diwawancara, pastikan bahwa sejak awal mereka memahami tentang apa itu Trash Hero dan tentang nilai-nilai positif inklusivitas yang kita gunakan. Disarankan juga untuk memeriksa tema yang akan mereka angkat sebelum Anda menyetujuinya.
Jika Anda dihubungi oleh media luar (TV, blogger, atau majalah) untuk diwawancara, pastikan bahwa sejak awal mereka memahami tentang apa itu Trash Hero dan tentang nilai-nilai positif inklusivitas yang kita gunakan. Disarankan juga untuk memeriksa tema yang akan mereka angkat sebelum Anda menyetujuinya. Jika Anda merasa grogi, cobalah untuk tetap tenang. Anda tidak harus menjadi juru bicara ahli, jawablah dari hati Anda, dan berpeganglah pada nilai-nilai yang Anda anggap benar. Anda dapat mempersiapkan diri dengan menonton beberapa video dan membaca artikel-artikel dari chapter Trash Hero lain untuk melihat bagaimana mereka melakukannya.
Jika Anda merasa grogi, cobalah untuk tetap tenang. Anda tidak harus menjadi juru bicara ahli, jawablah dari hati Anda, dan berpeganglah pada nilai-nilai yang Anda anggap benar. Anda dapat mempersiapkan diri dengan menonton beberapa video dan membaca artikel-artikel dari chapter Trash Hero lain untuk melihat bagaimana mereka melakukannya. Bagaimana cara mendekati pelaku usaha
Bagaimana cara mendekati pelaku usaha Jangan meminta terlalu banyak dukungan di awal kerjasama. Bisnis dapat mendonasikan sedikit terlebih dahulu, dan jika mereka senang dengan bentuk kerjasama dengan Anda, mereka akan memberi bantuan lebih. Sebagai contoh: mintalah 50 karung sampah atau 2 buah nanas untuk konsumsi di aksi bersih selanjutnya.
Jangan meminta terlalu banyak dukungan di awal kerjasama. Bisnis dapat mendonasikan sedikit terlebih dahulu, dan jika mereka senang dengan bentuk kerjasama dengan Anda, mereka akan memberi bantuan lebih. Sebagai contoh: mintalah 50 karung sampah atau 2 buah nanas untuk konsumsi di aksi bersih selanjutnya.


 Jalan menuju perubahan yang lebih baik dapat dipenuhi oleh rasa frustasi, kekecewaan, kebosanan, dan bahkan ketakutan. Ingatlah bahwa Anda memiliki keluarga besar Trash Hero di belakang Anda, dan bahwa membersihkan hal-hal negatif adalah keahlian kita 😉 Percayalah pada misi dan diri Anda, dan terimalah fakta bahwa memulai dan membawa perubahan membutuhkan waktu yang tidak sebentar.
Jalan menuju perubahan yang lebih baik dapat dipenuhi oleh rasa frustasi, kekecewaan, kebosanan, dan bahkan ketakutan. Ingatlah bahwa Anda memiliki keluarga besar Trash Hero di belakang Anda, dan bahwa membersihkan hal-hal negatif adalah keahlian kita 😉 Percayalah pada misi dan diri Anda, dan terimalah fakta bahwa memulai dan membawa perubahan membutuhkan waktu yang tidak sebentar.
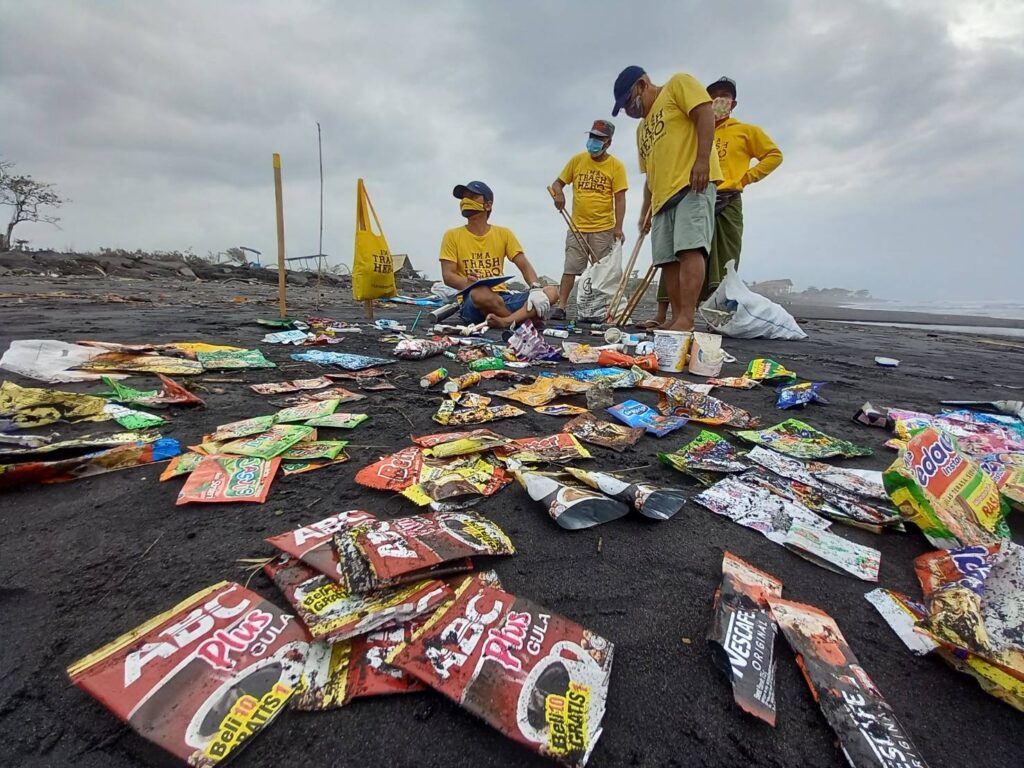
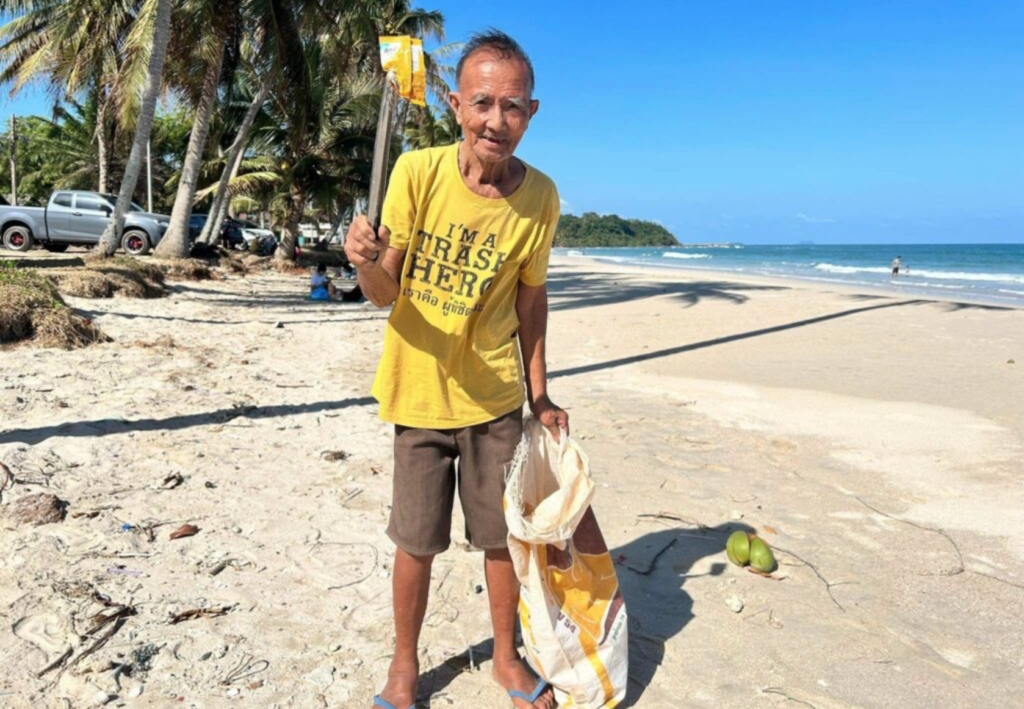
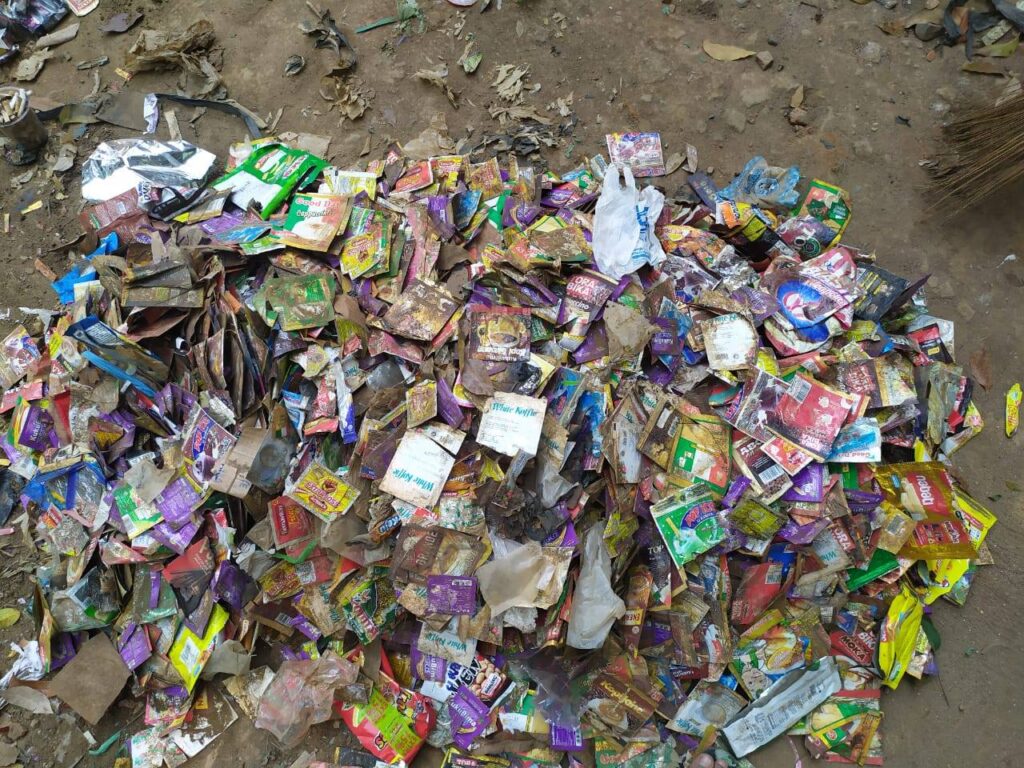
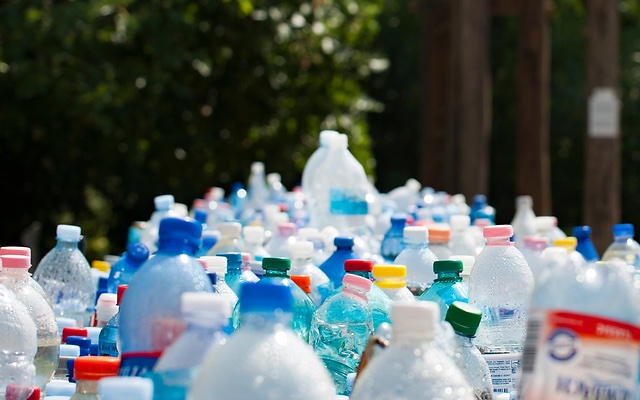
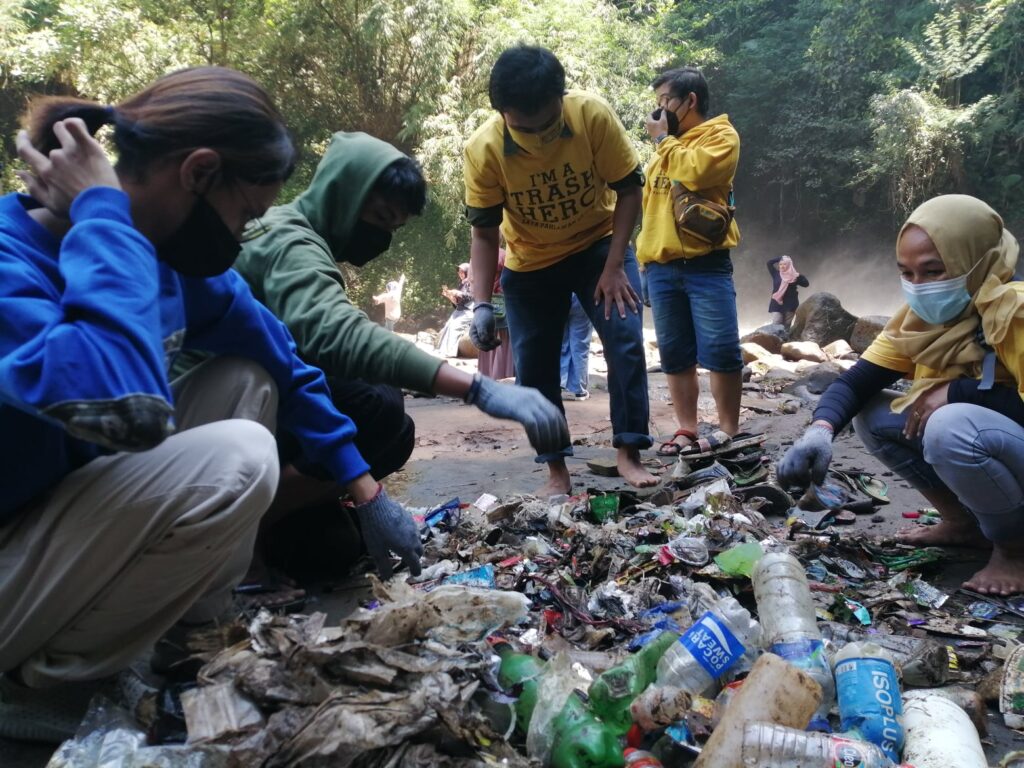

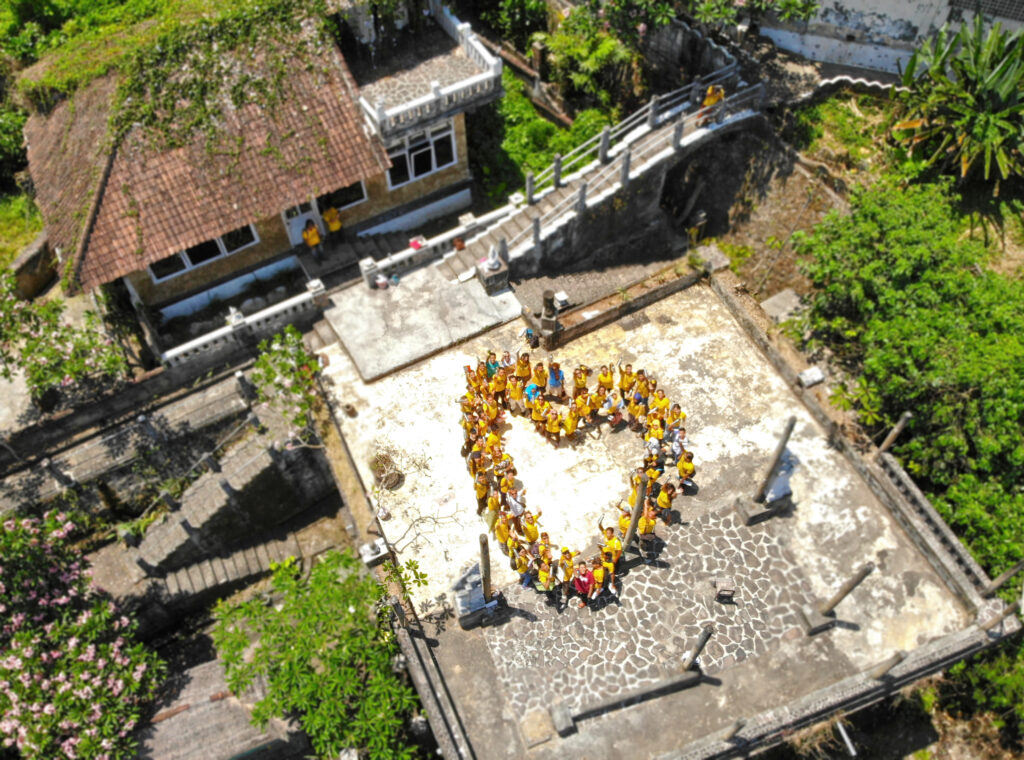














 Pembersihan
Pembersihan Botol dan Beg Ulang Pakai
Botol dan Beg Ulang Pakai Pendidikan & Kanak-kanak
Pendidikan & Kanak-kanak Pasukan yang baik adalah penting dalam kejayaan chapter anda. Ia harus mempunyai sekurang-kurangnya tiga orang, dan harus merangkumi seorang ahli yang mempunyai hubungan yang rapat dengan komuniti tempatan. Saiz optimum adalah 5-6 orang.
Pasukan yang baik adalah penting dalam kejayaan chapter anda. Ia harus mempunyai sekurang-kurangnya tiga orang, dan harus merangkumi seorang ahli yang mempunyai hubungan yang rapat dengan komuniti tempatan. Saiz optimum adalah 5-6 orang.
 Kami mempunyai garis panduan untuk penggunaan logo, warna dan fon kami, serta set templat untuk kegunaan bahan pemasaran utama. Anda boleh meminta akses kepada templat tersebut setelah anda menubuhkan chapter anda.
Kami mempunyai garis panduan untuk penggunaan logo, warna dan fon kami, serta set templat untuk kegunaan bahan pemasaran utama. Anda boleh meminta akses kepada templat tersebut setelah anda menubuhkan chapter anda.
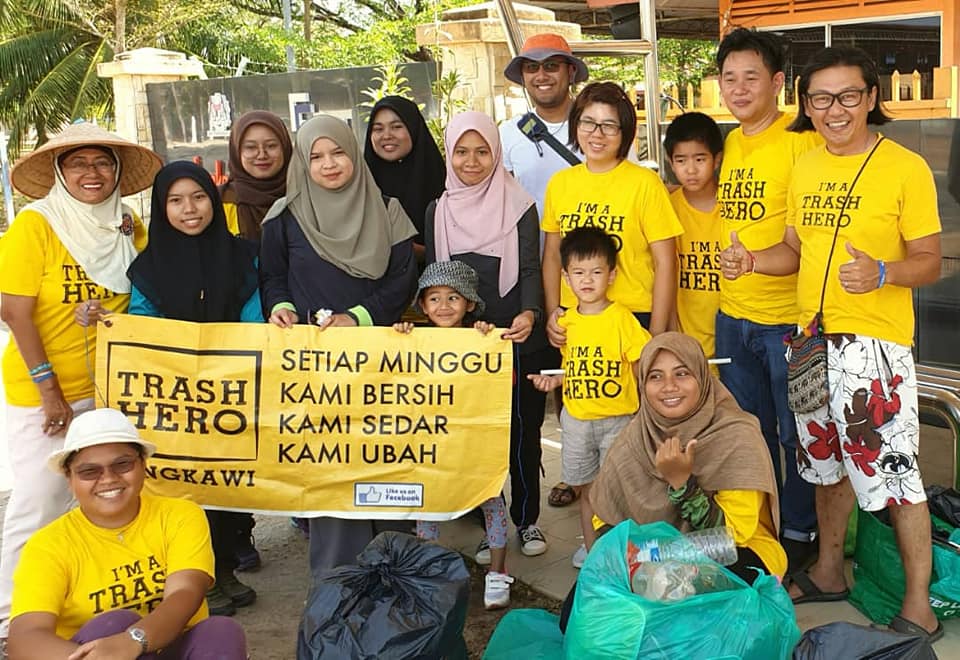


 Maklumkan orang ramai tentang pembersihan anda
Maklumkan orang ramai tentang pembersihan anda Terdapat pelbagai cara untuk kerjasama: perniagaan lokal atau perbandaran boleh menyediakan alatan pembersihan; kutipan sampah boleh dilakukan oleh perkhidmatan sampah tempatan; restoran atau hotel boleh memberikan air atau makanan untuk sukarelawan; kedai dobi boleh mencuci sarung tangan percuma dsbg. (Lihat juga:
Terdapat pelbagai cara untuk kerjasama: perniagaan lokal atau perbandaran boleh menyediakan alatan pembersihan; kutipan sampah boleh dilakukan oleh perkhidmatan sampah tempatan; restoran atau hotel boleh memberikan air atau makanan untuk sukarelawan; kedai dobi boleh mencuci sarung tangan percuma dsbg. (Lihat juga:  Buat taklimat: alu-alukan kedatangan semua orang dan berterima kasih kepada mereka kerana datang. Perkenalkan Trash Hero secara ringkas, dan terangkan misi dan organisasinya. Terangkan rancangan untuk hari ini (lihat perkara di atas). Ingatkan orang untuk berseronok, berehat seketika, minum air dan segala cebisan yang dikutip dikira. Jika anda ada baju Trash Hero, sekarang adalah masa yang sesuai untuk menyatakan ia dijual pada harga kos, supaya sukarelawan baharu boleh memakainya sewaktu pembersihan (dan anda mempunyai lebih banyak warna kuning dalam gambar!).
Buat taklimat: alu-alukan kedatangan semua orang dan berterima kasih kepada mereka kerana datang. Perkenalkan Trash Hero secara ringkas, dan terangkan misi dan organisasinya. Terangkan rancangan untuk hari ini (lihat perkara di atas). Ingatkan orang untuk berseronok, berehat seketika, minum air dan segala cebisan yang dikutip dikira. Jika anda ada baju Trash Hero, sekarang adalah masa yang sesuai untuk menyatakan ia dijual pada harga kos, supaya sukarelawan baharu boleh memakainya sewaktu pembersihan (dan anda mempunyai lebih banyak warna kuning dalam gambar!). Selepas pembersihan
Selepas pembersihan – tarikh pembersihan
– tarikh pembersihan
 Ini merupakan soalan lazim yang orang akan tanya pada setiap pembersihan Trash Hero. Jawapannya bergantung pada lokasi dan sistem pelupusan sisa yang terdapat di tempat anda.
Ini merupakan soalan lazim yang orang akan tanya pada setiap pembersihan Trash Hero. Jawapannya bergantung pada lokasi dan sistem pelupusan sisa yang terdapat di tempat anda.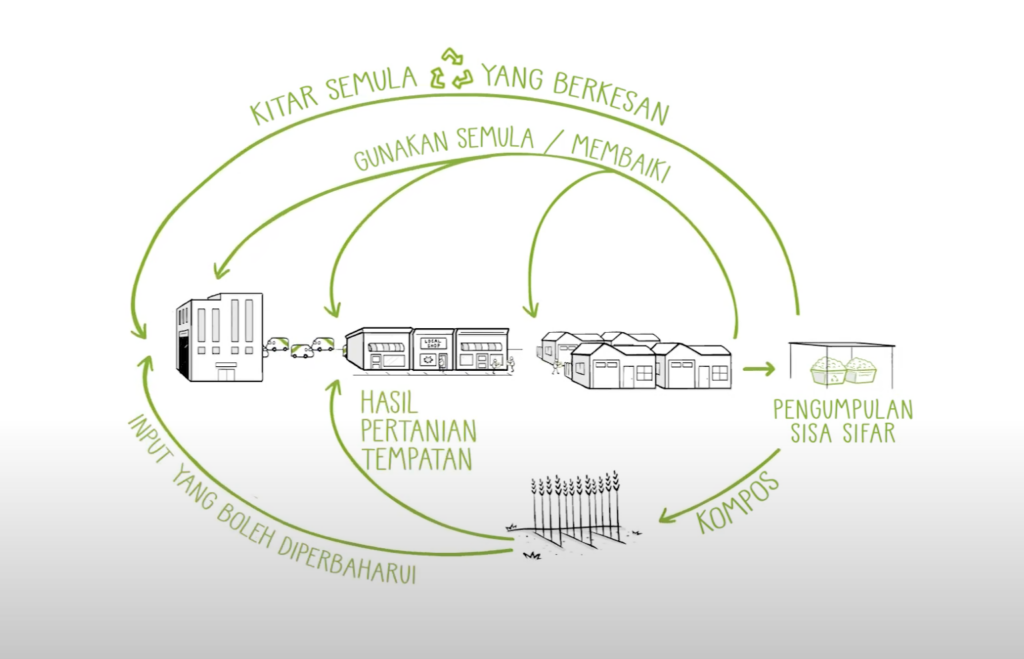
 Program ini menyediakan botol air keluli tahan karat yang di jual pada harga kos kepada peniaga tempatan, untuk dijual kembali kepada pelanggan mereka dengan sedikit keuntungan. Keuntungan ini akan digunakan untuk menyediakan air minuman percuma kepada pelanggan yang memiliki botol minuman Trash Hero, tanpa mengira di mana mereka membeli botol tersebut.
Program ini menyediakan botol air keluli tahan karat yang di jual pada harga kos kepada peniaga tempatan, untuk dijual kembali kepada pelanggan mereka dengan sedikit keuntungan. Keuntungan ini akan digunakan untuk menyediakan air minuman percuma kepada pelanggan yang memiliki botol minuman Trash Hero, tanpa mengira di mana mereka membeli botol tersebut. Ia kini, dikilangkan di China, sementara kami berusaha mencari pengeluar tempatan. Trash Hero mempunyai sijil kualiti dan komposisi bahan bagi botol yang tersedia untuk ditunjukkan kepada rakan kongsi dan pelanggan mereka.
Ia kini, dikilangkan di China, sementara kami berusaha mencari pengeluar tempatan. Trash Hero mempunyai sijil kualiti dan komposisi bahan bagi botol yang tersedia untuk ditunjukkan kepada rakan kongsi dan pelanggan mereka.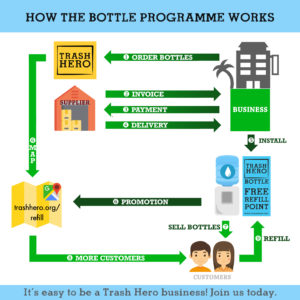
 Media sosial
Media sosial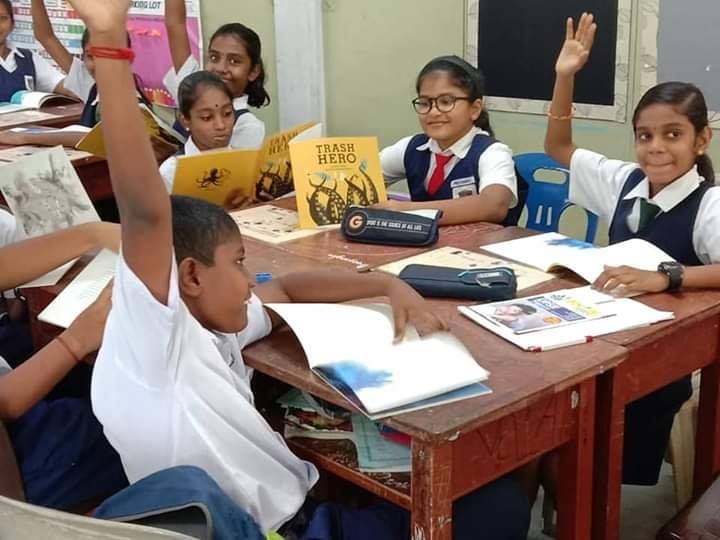
 Selalunya terdapat acara hotel atau persatuan perdagangan di mana anda boleh melakukan pembentangan dan menunjukkan kepada syarikat bagaimana untuk mengambil tindakan. Tanya sama ada mereka akan memberi informasi kepada ahli mereka untuk memperkenalkan Trash Hero dan jemput mereka untuk menghantar kakitangan ke pembersihan atau menyediakan perkhidmatan untuk anda.
Selalunya terdapat acara hotel atau persatuan perdagangan di mana anda boleh melakukan pembentangan dan menunjukkan kepada syarikat bagaimana untuk mengambil tindakan. Tanya sama ada mereka akan memberi informasi kepada ahli mereka untuk memperkenalkan Trash Hero dan jemput mereka untuk menghantar kakitangan ke pembersihan atau menyediakan perkhidmatan untuk anda. Bekerjasama dengan organisasi bukan berkeuntungan lain atau projek alam sekitar di kawasan anda atau di seluruh dunia. Kami tidak bersaing dengan sesiapa: hanya dengan bekerjasama, kita boleh membuat perbezaan.
Bekerjasama dengan organisasi bukan berkeuntungan lain atau projek alam sekitar di kawasan anda atau di seluruh dunia. Kami tidak bersaing dengan sesiapa: hanya dengan bekerjasama, kita boleh membuat perbezaan. Sekiranya anda mempunyai hubungan yang baik dengan kerajaan tempatan anda, anda boleh cuba menambah baik kutipan sampah sedia ada dengan membawa orang yang tepat dalam komuniti bersama-sama untuk berbincang dan melaksanakan penyelesaian, misalnya dengan menyediakan lebih banyak tong sampah awam.
Sekiranya anda mempunyai hubungan yang baik dengan kerajaan tempatan anda, anda boleh cuba menambah baik kutipan sampah sedia ada dengan membawa orang yang tepat dalam komuniti bersama-sama untuk berbincang dan melaksanakan penyelesaian, misalnya dengan menyediakan lebih banyak tong sampah awam. Libatkan diri dalam festival tempatan: nasihatkan penganjur bagaimana untuk menjalankan sisa sifar atau meletakkan lebih banyak tong sampah di sekitar kawasan tersebut. Bantu mereka untuk menganjurkan acara pembersihan dengan kakitangan mereka selepas itu tetapi pastikan mereka juga membuat komitmen untuk meningkatkan pengurusan sisa mereka semasa festival.
Libatkan diri dalam festival tempatan: nasihatkan penganjur bagaimana untuk menjalankan sisa sifar atau meletakkan lebih banyak tong sampah di sekitar kawasan tersebut. Bantu mereka untuk menganjurkan acara pembersihan dengan kakitangan mereka selepas itu tetapi pastikan mereka juga membuat komitmen untuk meningkatkan pengurusan sisa mereka semasa festival.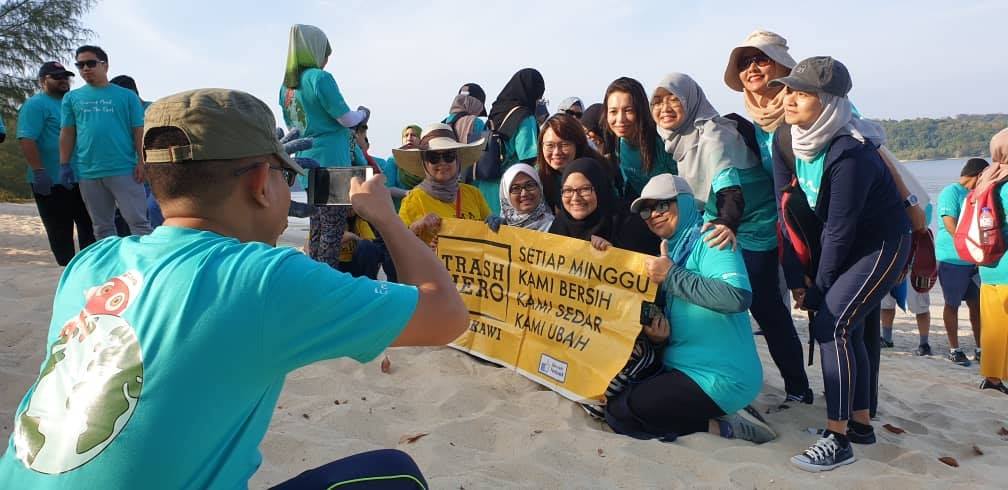
 Jika anda dihubungi oleh mana-mana media luaran (TV, blog, majalah) untuk ditemu bual, pastikan mereka jelas terlebih dahulu apa itu Trash Hero dan pendekatan positif dan inklusif kita. Ia juga berguna untuk menyemak mesej yang mereka maksudkan sebelum anda bersetuju. Sebagai contoh, kami menemui sebuah saluran berita tempatan yang ingin memberi tumpuan kepada pasangan orang asing yang mereka lihat semasa pembersihan, untuk mencuba dan “memalukan” penduduk tempatan bahawa orang barat membersihkan pantai mereka, dan bukannya mengiktiraf bahawa terdapat usaha komuniti yang berlaku.
Jika anda dihubungi oleh mana-mana media luaran (TV, blog, majalah) untuk ditemu bual, pastikan mereka jelas terlebih dahulu apa itu Trash Hero dan pendekatan positif dan inklusif kita. Ia juga berguna untuk menyemak mesej yang mereka maksudkan sebelum anda bersetuju. Sebagai contoh, kami menemui sebuah saluran berita tempatan yang ingin memberi tumpuan kepada pasangan orang asing yang mereka lihat semasa pembersihan, untuk mencuba dan “memalukan” penduduk tempatan bahawa orang barat membersihkan pantai mereka, dan bukannya mengiktiraf bahawa terdapat usaha komuniti yang berlaku. Bagaimana untuk mendekati perniagaan
Bagaimana untuk mendekati perniagaan Pada permulaan, jangan meminta terlalu banyak bantuan. Perniagaan boleh menderma sedikit dan apabila mereka gembira mereka akan membantu lebih banyak. Sebagai contoh: minta 30 beg sampah atau buah-buahan untuk pembersihan seterusnya.
Pada permulaan, jangan meminta terlalu banyak bantuan. Perniagaan boleh menderma sedikit dan apabila mereka gembira mereka akan membantu lebih banyak. Sebagai contoh: minta 30 beg sampah atau buah-buahan untuk pembersihan seterusnya.
 Terus meraikan
Terus meraikan Jalan ke arah memberi impak positif boleh dipenuhi dengan kekecewaan, kebosanan, atau ketakutan. Ingat bahawa anda mempunyai keluarga besar Trash Hero di belakang anda dan membersihkan hal-hal negatif adalah kepakaran kita 😉
Jalan ke arah memberi impak positif boleh dipenuhi dengan kekecewaan, kebosanan, atau ketakutan. Ingat bahawa anda mempunyai keluarga besar Trash Hero di belakang anda dan membersihkan hal-hal negatif adalah kepakaran kita 😉