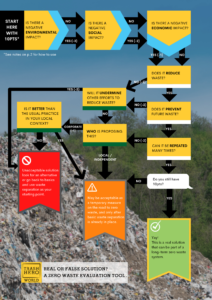
One of the main – and most effective – measures to control the spread of COVID-19 is the use of face masks. Placed over the nose and mouth, their function is to contain respiratory droplets which transmit the virus and stop them spreading to other people. There are various grades of mask, but it is widely accepted that outside of a clinical situation, fabric, non-medical masks provide an acceptable level of protection – single-use, surgical masks are not necessary.
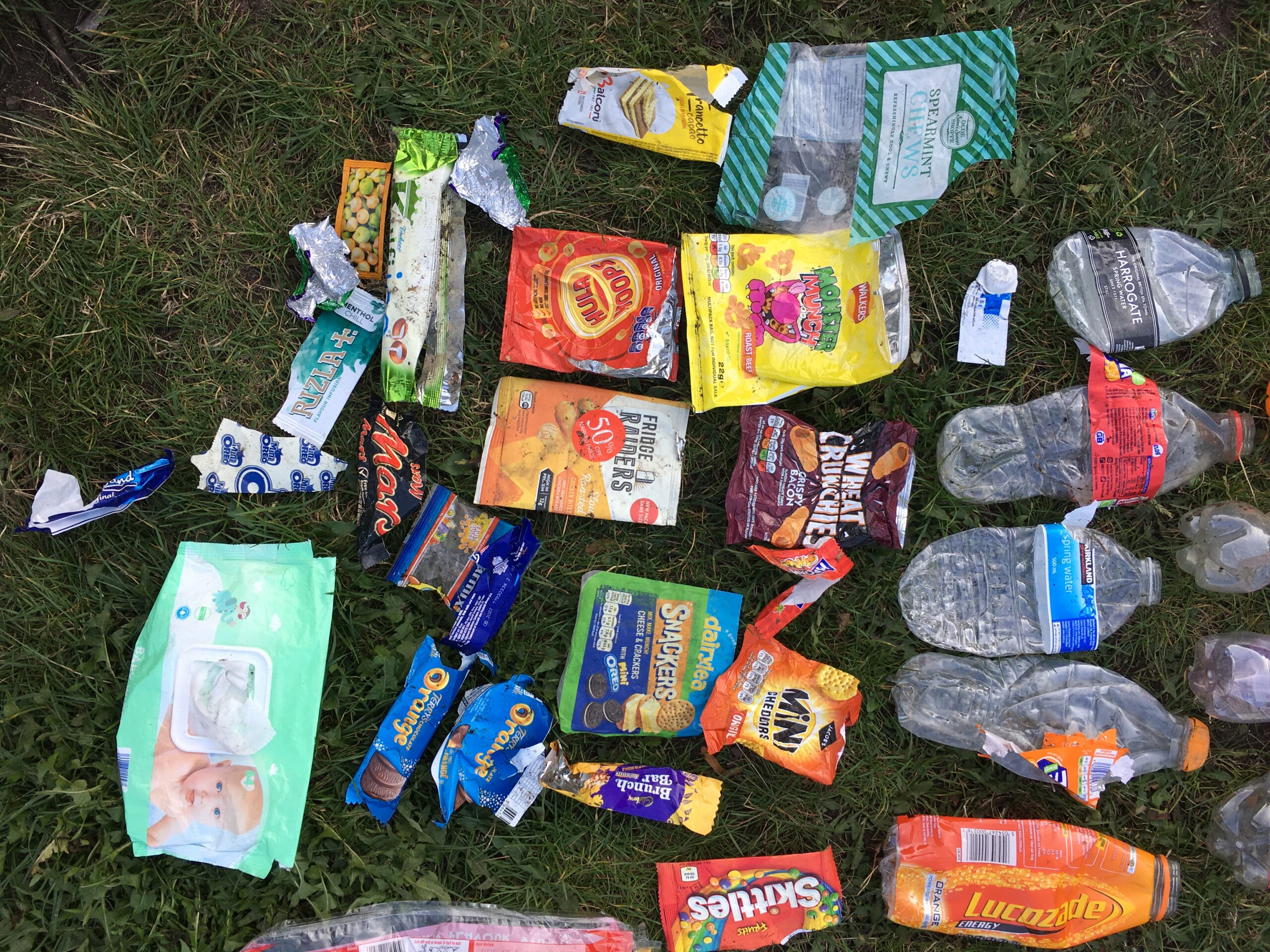
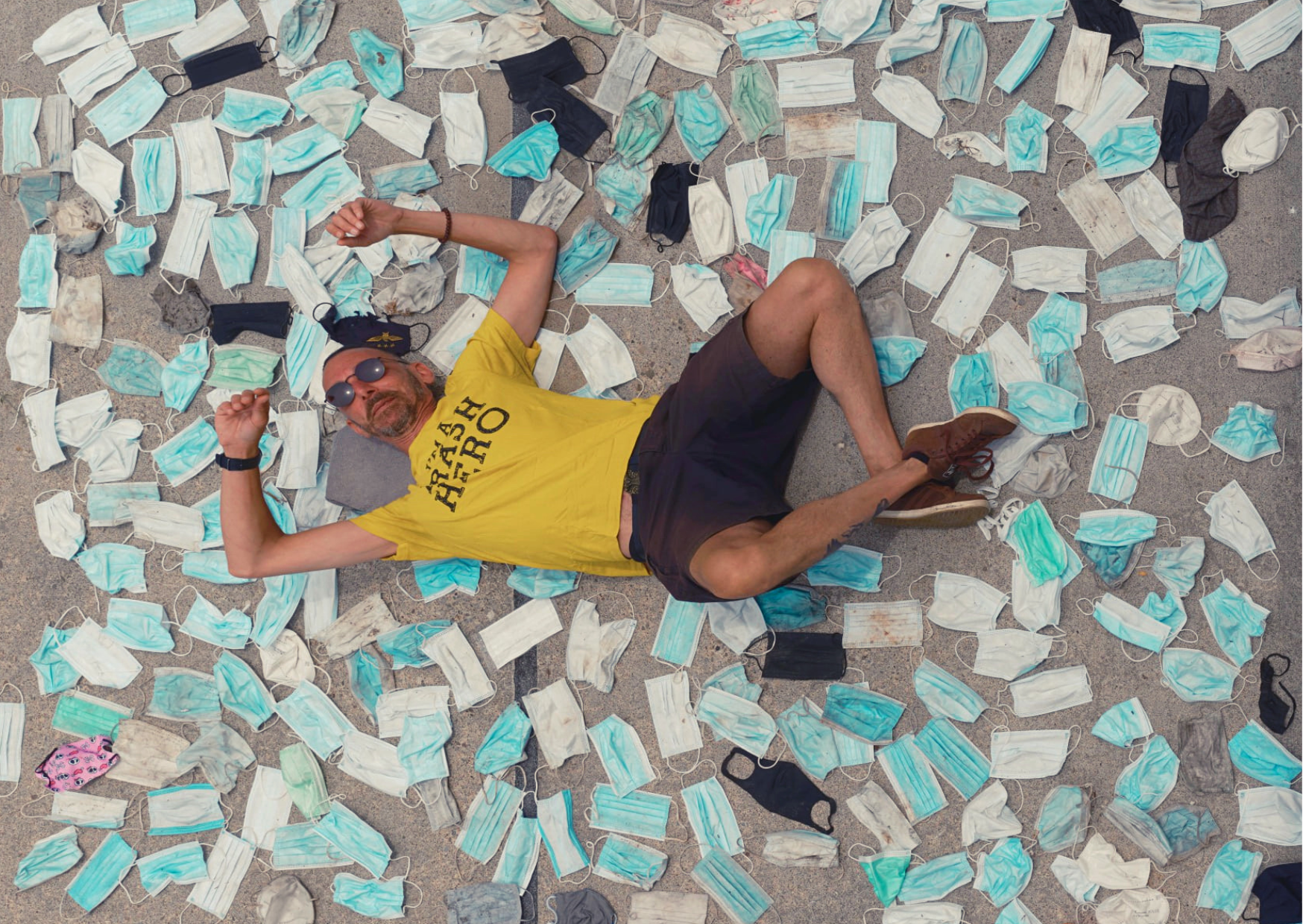
Yet globally we are using an estimated 129 billion single-use masks every month. Assuming each of these weighs 4 grams, that’s 516,000 metric tons of unrecyclable, hazardous waste generated every 30 or so days. If only 1% of this ends up as litter (a conservative estimate), that means 23 billion masks have entered our rivers, oceans and forests in the 18 months since the pandemic began. And of course, there are hundreds of thousands of tons of additional contaminated waste for municipalities to handle, assuming they have the capacity to do so.
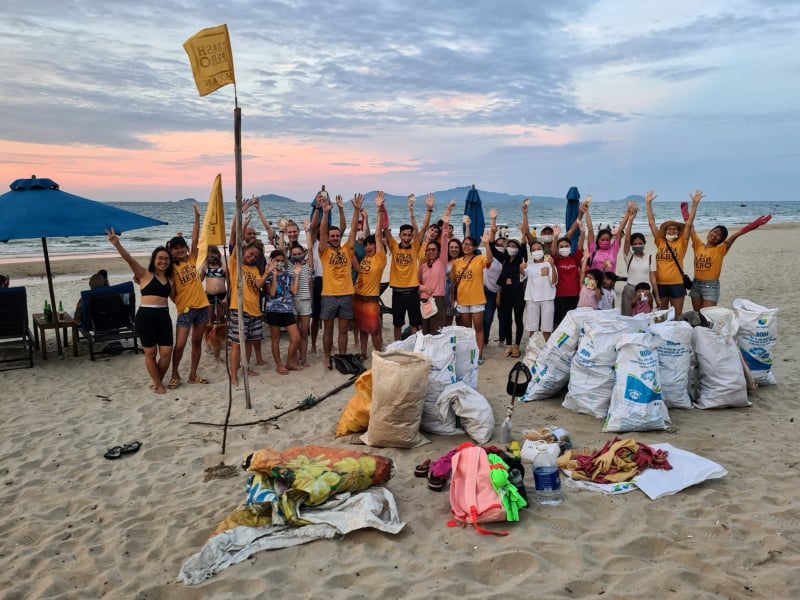
These are frightening statistics – and ones that are borne out by our experience doing cleanups all over the world in 2020 and 2021. Trash Hero chapters pick up single-use masks and other PPE every week – and their findings have been covered in the media. This month, we put in place a system to record the number of masks we find at the network level, in order to raise awareness about what we see as the triple threat of single-use masks.
Research has shown that single-use masks not only have devastating impacts on the environment, but also on society and on our health.
 WHERE DO THEY GO?
WHERE DO THEY GO?
Single-use masks are made from plastic, usually polypropylene or polyurethane, and are considered unrecyclable. But they should not be disposed of loose in the general waste, due to the risk of contamination. According to the World Health Organisation, they need to be double bagged in yet more plastic.
Cities and local communities have had to deal with the outcomes: the health risk from incorrect disposal as well as a huge burden of non-recyclable waste – if a waste management infrastructure even exists, which is not the case in much of the Global South.
Face masks used in a clinical setting are handled by special waste management facilities that deal with medical waste – usually through incineration. It is unusual for separate PPE collection facilities to exist for the general public, but if they do, it means rates of unsustainable and toxic incineration have increased proportionally.
 HEALTH RISKS
HEALTH RISKS
A recent study has shown that tiny microplastics are shed from single-use masks both during and after use. Aside from the wearer inhaling these microplastics at close range (with unknown impacts on their health), contaminated nano-particles are being released into the surroundings. Once airborne, these particles can be carried up to 95km away from the source.
The SARS-CoV-2 virus (responsible for COVID-19) is able to survive much longer on the surface of plastic (around 3 days) than in respiratory droplets (around 3 hours). This means that single-use mask fibres are a transmission vector for the virus, extending its reach over longer times and distances. According to the report’s authors, “the transmission route through airborne microplastics is expected to influence, not only individual countries, but also larger regions and the whole world.”
 ENVIRONMENTAL RISKS
ENVIRONMENTAL RISKS
Finally the impact on the natural environment from single-use masks is much the same as any other plastic. Wherever they end up, on land or in the ocean, they can entangle wildlife and cause poisoning through ingestion (that is carried up the food chain). Their slow demise into microplastics happens over centuries, all the while leaching toxic chemicals into the water or soil.
 ALL OF THIS IS AVOIDABLE!.
ALL OF THIS IS AVOIDABLE!.
When not in a clinical environment, or not clinically vulnerable, switch to a reusable mask: wear, wash and repeat. If made from multi-layered thick cotton, a reusable mask can be used safely for years and has minimal impact on the environment, especially if made from material you already have.
read more
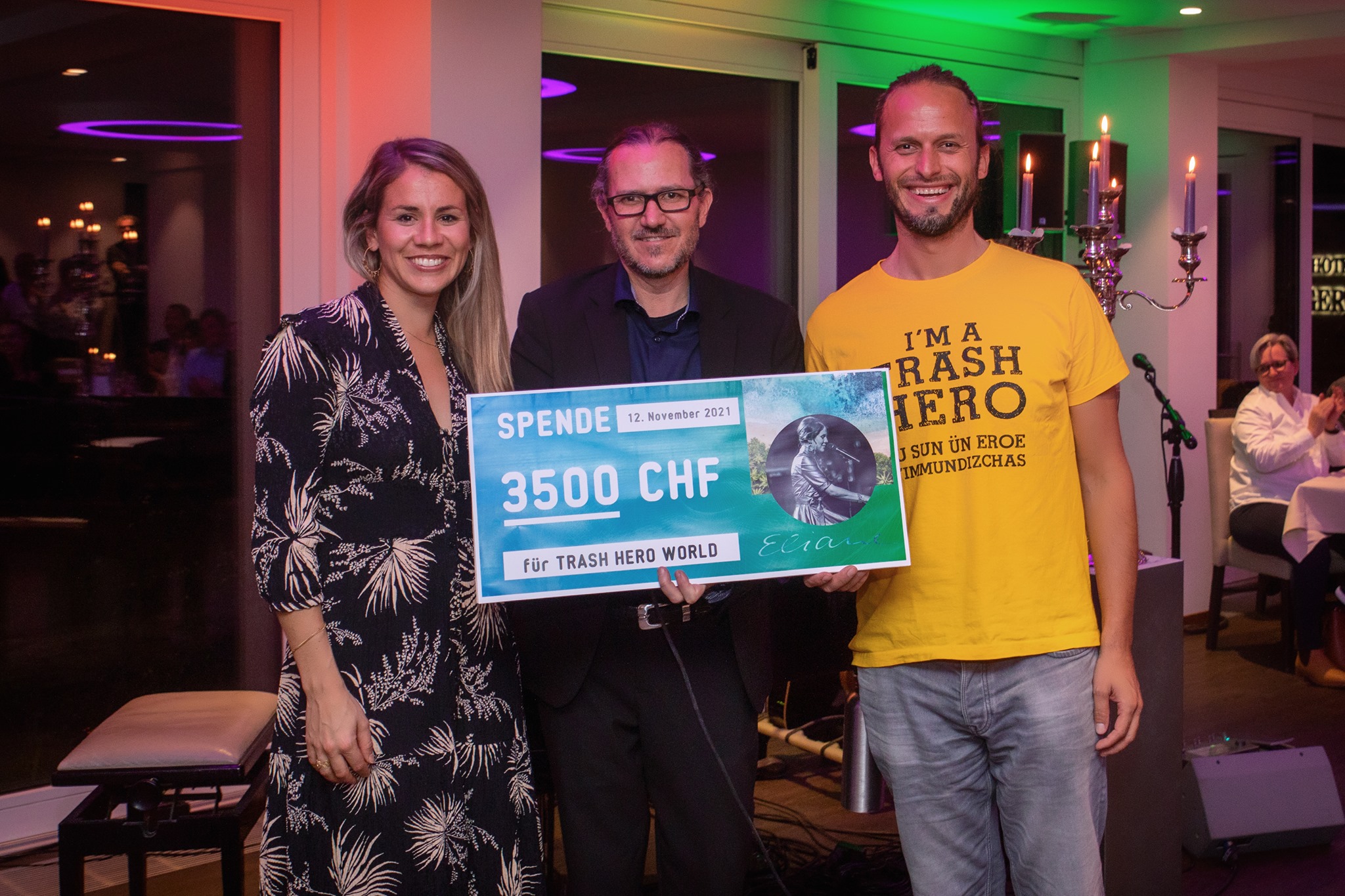
 A piano and guitar set was performed by a Swiss singer and song-writer Eliane, winner of the second season of Switzerland’s Got Talent. Eliane is an ambassador for Schnarwiler’s cosmetics lines “Trash Hero Love” and “Re-use-me” and is an avid supporter of Trash Hero’s activities.
A piano and guitar set was performed by a Swiss singer and song-writer Eliane, winner of the second season of Switzerland’s Got Talent. Eliane is an ambassador for Schnarwiler’s cosmetics lines “Trash Hero Love” and “Re-use-me” and is an avid supporter of Trash Hero’s activities.  The gala was organised by Schnarwiler, a Swiss based manufacturer and distributor of beauty and health products, who have launched a zero-waste line of toiletry products in collaboration with Trash Hero. During the event, Roman Peter had the opportunity to deliver a presentation to an audience of around 100 people, explaining the mission and vision of Trash Hero, as well as inviting attendees to join the movement.
The gala was organised by Schnarwiler, a Swiss based manufacturer and distributor of beauty and health products, who have launched a zero-waste line of toiletry products in collaboration with Trash Hero. During the event, Roman Peter had the opportunity to deliver a presentation to an audience of around 100 people, explaining the mission and vision of Trash Hero, as well as inviting attendees to join the movement. 












 WHERE DO THEY GO?
WHERE DO THEY GO? HEALTH RISKS
HEALTH RISKS ENVIRONMENTAL RISKS
ENVIRONMENTAL RISKS ALL OF THIS IS AVOIDABLE!.
ALL OF THIS IS AVOIDABLE!.